Stargaze 
VirtualBox Power Driver for MAAS (Metal as a Service)
A way to manage the power of VirtualBox virtual machines via the MAAS webhook driver.
MAAS (Metal as a Service) is a tool to turns real servers into bare-metal cloud. With MAAS, you can automate server provisioning and installing OS remotely on both physical and virtual servers. MAAS.io for more information.
vboxpower is a wrapper to enabling MAAS to manage VirtualBox virtual machines power directly. As you know, MAAS does not natively support VirtualBox power management. Before vboxpower, you had to use manual power type for VirtualBox machines, the process of starting/stopping virtual machines did manually but with vboxpower this process is done automatically. So to speak, the prophecy of the vboxpower is translating power commands between VirtualBox and MAAS.
Both MAAS and vboxpower are written in Python language. So, you don't need another language to run vboxpower.
- VirtualBox 6+ installed and running.
- VirtualBox SDK https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
- VirtualBox Extension Pack to support PXE boot.
Download and extract VirtualBox SDK and run the following command.
sudo VBOX_INSTALL_PATH=/usr/lib/virtualbox python3 vboxapisetup.py installTo deploy vboxpower, you need python3-pip to install the required packages.
The deploy script creates systemd service and copies vboxpower.py to /opt/maas/vboxpower directory.
After deployment, the deploy script starts the vboxpower service.
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y python3-pip python3
sudo ./deployThe vboxpower is listening on port 5241/tcp on all interfaces.
You should be able to see the list of available VirtualBox virtual machines with curl command.
curl 192.168.56.1:5241
{
"machines": [
{
"links": {
"off": "/pfsense/off",
"on": "/pfsense/on",
"status": "/pfsense/status"
},
"name": "pfsense",
"status": "running"
},
{
"links": {
"off": "/maas/off",
"on": "/maas/on",
"status": "/maas/status"
},
"name": "maas",
"status": "running"
}
]
}Each virtual machine exposes three endpoints that are used for vm power management.
- http://HOST_IP:5241/VM_NAME/on
- http://HOST_IP:5241/VM_NAME/off
- http://HOST_IP:5241/VM_NAME/status
Use these endpoints on MAAS Webhook power URI, respectively.
I have tested the process on Ubuntu 20.04, MAAS 3.0, and VirtualBox 6.1.16 completely.
Other versions should be work without problem.
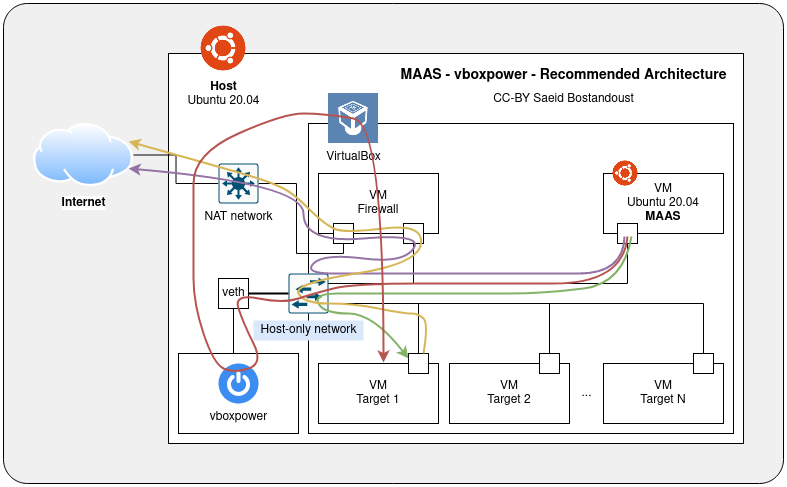
If you want to deploy MAAS inside a virtual machine as well, I recommend you to make an environment like the following architecture. In this architecture, you need two virtual machines to create the MAAS stack. The former is a firewall which I suggest use pfSense, OpenWrt, Ubuntu (MASQUERADE), and the latter is a virtual machine that the MAAS is deployed on that. In addition to these essential virtual machines, create target virtual machines, the machines that you want to be deployed by the MAAS platform.
The path shows the path of the way the MAAS machine accesses the internet.
The path shows the path of power management of the target machine.
The path shows the path of how the MAAS deploys the target machine.
The path shows the path of the way the target machine accesses the internet.
All contributions are welcomed. If you find any bugs, please file an issue.
Copyright 2021 Saeid Bostandoust ssbostan@linuxmail.org