Apriori
Apriori is an algorithm for frequent item set mining and association rule learning over relational databases. It proceeds by identifying the frequent individual items in the database and extending them to larger and larger item sets as long as those item sets appear sufficiently often in the database. The frequent item sets determined by Apriori can be used to determine association rules which highlight general trends in the database: this has applications in domains such as market basket analysis.
Apriori(T, ε)
L1 ← {large 1 - itemsets}
k ← 2
while Lk−1 is not empty
Ck ← Apriori_gen(Lk−1, k)
for transactions t in T
Dt ← {c in Ck : c ⊆ t}
for candidates c in Dt
count[c] ← count[c] + 1
Lk ← {c in Ck : count[c] ≥ ε}
k ← k + 1
return Union(Lk)
Apriori_gen(L, k)
result ← list()
for all p ⊆ L, q ⊆ L where p1 = q1, p2 = q2, ..., pk-2 = qk-2 and pk-1 < qk-1
c = p ∪ {qk-1}
if u ⊆ c for all u in L
result.add(c)
return result
DB Usage
I used Database in my project and i store that data in 'kosarak.csv' in DB folder.
CLI Usage
For run this project in your computer, you should enter below command in your cmd:
python ./Src/apriori.py -f ./DB/kosarak.csv
Apriori Algorithm
- Difficulty Level : Medium
- Last Updated : 04 Apr, 2020
Prerequisite – Frequent Item set in Data set (Association Rule Mining)
Apriori algorithm is given by R. Agrawal and R. Srikant in 1994 for finding frequent itemsets in a dataset for boolean association rule. Name of the algorithm is Apriori because it uses prior knowledge of frequent itemset properties. We apply an iterative approach or level-wise search where k-frequent itemsets are used to find k+1 itemsets.
To improve the efficiency of level-wise generation of frequent itemsets, an important property is used called Apriori property which helps by reducing the search space.
Apriori Property –
All non-empty subset of frequent itemset must be frequent. The key concept of Apriori algorithm is its anti-monotonicity of support measure. Apriori assumes that
All subsets of a frequent itemset must be frequent(Apriori propertry).
If an itemset is infrequent, all its supersets will be infrequent.
Before we start understanding the algorithm, go through some definitions which are explained in my previous post.
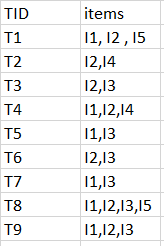
Consider the following dataset and we will find frequent itemsets and generate association rules for them.
Step-1: K=1
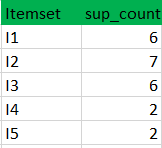
(I) Create a table containing support count of each item present in dataset – Called C1(candidate set)
(II) compare candidate set item’s support count with minimum support count(here min_support=2 if support_count of candidate set items is less than min_support then remove those items). This gives us itemset L1.
Step-2: K=2
- Generate candidate set C2 using L1 (this is called join step). Condition of joining Lk-1 and Lk-1 is that it should have (K-2) elements in common.
- Check all subsets of an itemset are frequent or not and if not frequent remove that itemset.(Example subset of{I1, I2} are {I1}, {I2} they are frequent.Check for each itemset)
- Now find support count of these itemsets by searching in dataset.
(II) compare candidate (C2) support count with minimum support count(here min_support=2 if support_count of candidate set item is less than min_support then remove those items) this gives us itemset L2.
Step-3:
- Generate candidate set C3 using L2 (join step). Condition of joining Lk-1 and Lk-1 is that it should have (K-2) elements in common. So here, for L2, first element should match.
So itemset generated by joining L2 is {I1, I2, I3}{I1, I2, I5}{I1, I3, i5}{I2, I3, I4}{I2, I4, I5}{I2, I3, I5} - Check if all subsets of these itemsets are frequent or not and if not, then remove that itemset.(Here subset of {I1, I2, I3} are {I1, I2},{I2, I3},{I1, I3} which are frequent. For {I2, I3, I4}, subset {I3, I4} is not frequent so remove it. Similarly check for every itemset)
- find support count of these remaining itemset by searching in dataset.
(II) Compare candidate (C3) support count with minimum support count(here min_support=2 if support_count of candidate set item is less than min_support then remove those items) this gives us itemset L3.
Step-4:
- Generate candidate set C4 using L3 (join step). Condition of joining Lk-1 and Lk-1 (K=4) is that, they should have (K-2) elements in common. So here, for L3, first 2 elements (items) should match.
- Check all subsets of these itemsets are frequent or not (Here itemset formed by joining L3 is {I1, I2, I3, I5} so its subset contains {I1, I3, I5}, which is not frequent). So no itemset in C4
- We stop here because no frequent itemsets are found further
Thus, we have discovered all the frequent item-sets. Now generation of strong association rule comes into picture. For that we need to calculate confidence of each rule.Confidence –
A confidence of 60% means that 60% of the customers, who purchased milk and bread also bought butter.Confidence(A->B)=Support_count(A∪B)/Support_count(A)So here, by taking an example of any frequent itemset, we will show the rule generation.
Itemset {I1, I2, I3} //from L3
SO rules can be
[I1^I2]=>[I3] //confidence = sup(I1^I2^I3)/sup(I1^I2) = 2/4*100=50%
[I1^I3]=>[I2] //confidence = sup(I1^I2^I3)/sup(I1^I3) = 2/4*100=50%
[I2^I3]=>[I1] //confidence = sup(I1^I2^I3)/sup(I2^I3) = 2/4*100=50%
[I1]=>[I2^I3] //confidence = sup(I1^I2^I3)/sup(I1) = 2/6*100=33%
[I2]=>[I1^I3] //confidence = sup(I1^I2^I3)/sup(I2) = 2/7*100=28%
[I3]=>[I1^I2] //confidence = sup(I1^I2^I3)/sup(I3) = 2/6*100=33%So if minimum confidence is 50%, then first 3 rules can be considered as strong association rules.
Limitations of Apriori Algorithm
Apriori Algorithm can be slow. The main limitation is time required to hold a vast number of candidate sets with much frequent itemsets, low minimum support or large itemsets i.e. it is not an efficient approach for large number of datasets. For example, if there are 10^4 from frequent 1- itemsets, it need to generate more than 10^7 candidates into 2-length which in turn they will be tested and accumulate. Furthermore, to detect frequent pattern in size 100 i.e. v1, v2… v100, it have to generate 2^100 candidate itemsets that yield on costly and wasting of time of candidate generation. So, it will check for many sets from candidate itemsets, also it will scan database many times repeatedly for finding candidate itemsets. Apriori will be very low and inefficiency when memory capacity is limited with large number of transactions. [Source : https://arxiv.org/pdf/1403.3948.pdf]My Personal Notes arrow_drop_upSave - Generate candidate set C3 using L2 (join step). Condition of joining Lk-1 and Lk-1 is that it should have (K-2) elements in common. So here, for L2, first element should match.