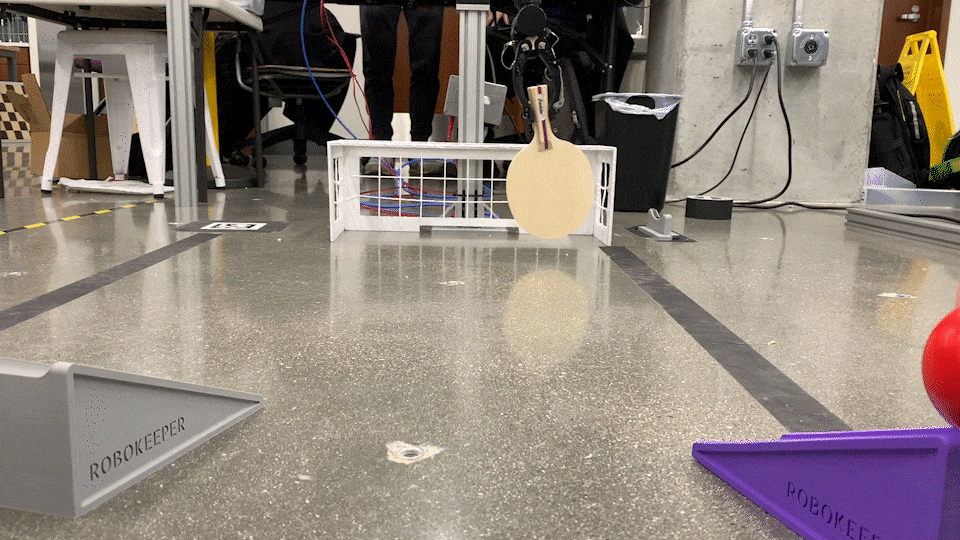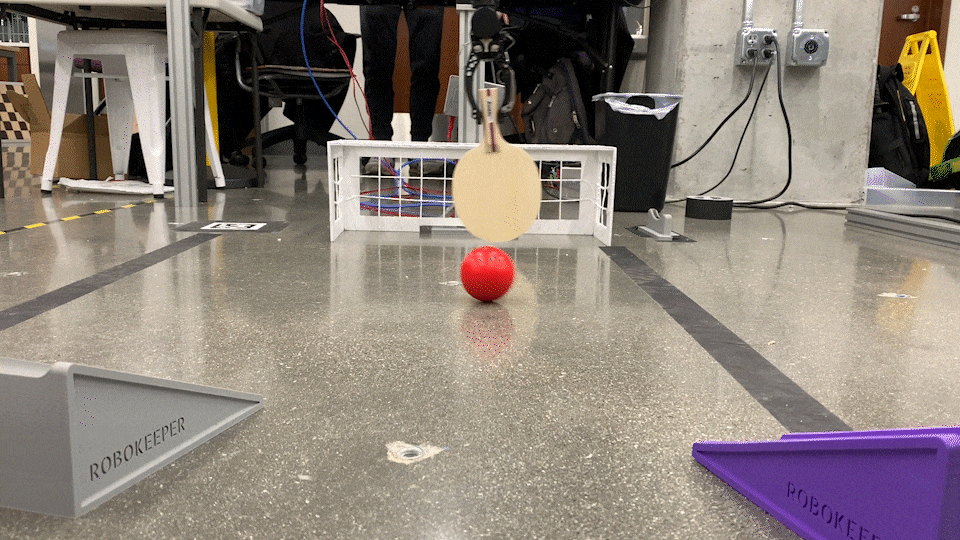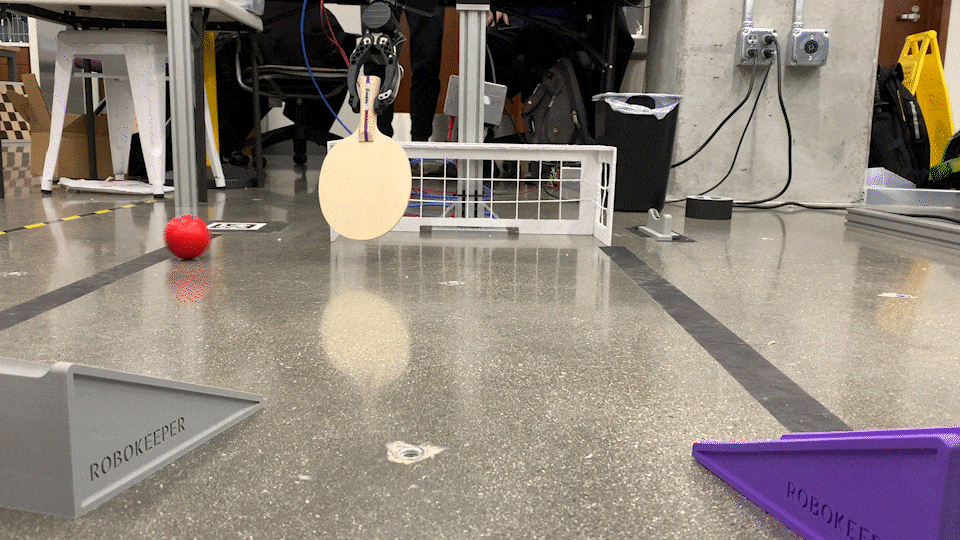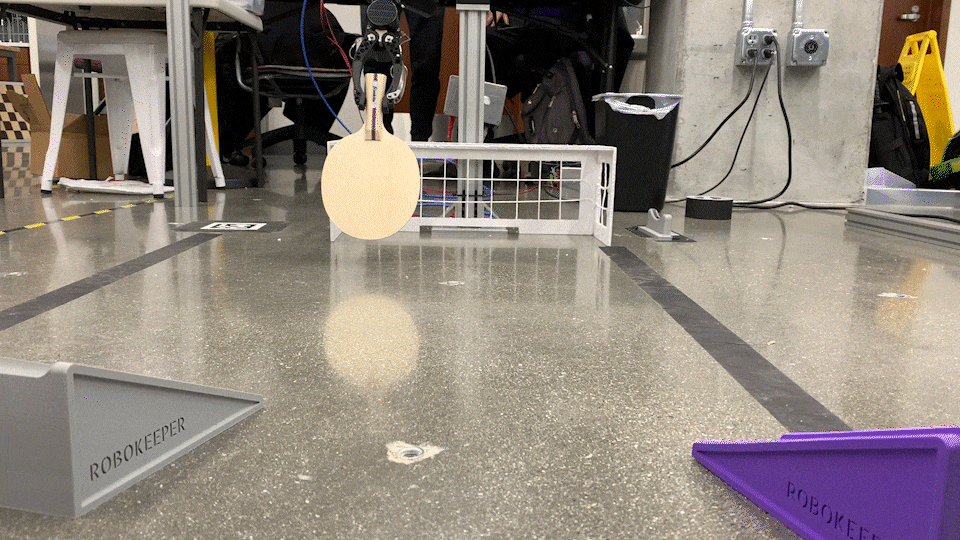
RoboKeeper!
Jonny Bosnich, Joshua Cho, Lio Liang, Marco Morales, Cody Nichoson
Demonstration Videos
- Grabbing the paddle: https://youtu.be/N0HPvFNHrTw
- Blocking the ball: https://youtu.be/9TuFG5CqvZ8
Equipment
Hardware:
- HDT Global Adroit Manipulator Arm
- Intel RealSense Camera
Software:
- Robot Operating System (ROS)
- MoveIt!
- OpenCV
- AprilTag
Quickstart Guide
- Install ROS Noetic on Ubuntu 20.04
- Create catkin workspace
$ source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash $ mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src $ cd ~/catkin_ws/ $ catkin_make - Copy this repository into
srcfolder$ cd ~/catkin_ws/src $ git clone [email protected]:ME495-EmbeddedSystems/final-project-robokeeper.git - Install required packages and build
$ source devel/setup.bash $ rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y $ catkin_make
Running the package
-
First, run the main launchfile. To run the program on the real robot, run the command below.
roslaunch robokeeper robokeeper_go.launch -
If using a simulation, add the
sim:=trueargument when running the main launchfile.roslaunch robokeeper robokeeper_go.launch sim:=true -
The robot now has to pick up the paddle and this is done with two services. First, call
above_paddle.rosservice call /above_paddle -
Next, call the 'retrieve_paddle` service.
rosservice call /retrieve_paddle -
Call the
resetservice to move the robot in front of the goal.rosservice call /reset -
Call
start_keepingto enable the goal keeping component of the project.rosservice call /start_keeping -
When finished, call the 'stop_keeping' service.
rosservice call /stop_keeping
Launchfiles
robokeeper_go.launch
This is the main launchfile used to operate robokeeper. It starts by launching robokeeper_moveit.launch which loads the necessary urdf file and hardware configuration, as well as the main MoveIt! executable. It then launches intel_cam.launch which starts the Intel Realsense camera. It also starts a transforms node which handles the calculation of transformation between various frames within the world. Finally, the launchfile starts a motion_control node that publishes appropriate joint state messages to actuate the arm.
robokeeper_moveit.launch
This launchfile loads robot description for the Adroit 6-dof manipulator arm, as well as its hardware and controller configuration from the hdt_6dof_a24_pincer_description package. It also includes move_group.launch from the hdt_6dof_a24_pincer_moveit package, which starts the move group that MoveIt! uses to plan the motion of the arm.
intel_cam.launch
This launchfile starts the Intel Realsense camera by launching rs_camera.launch from the realsense2_camera package. It then launches AprilTag_detection.launch for AprilTag integration.
AprilTag_detection.launch
This launchfile loads parameters necessary for integrating AprilTag detection, which is crucial for detecting the position of the robot relative to the camera. It starts apriltag_ros_continuous_node from the apriltag_ros package.
Nodes
perception
The perception node is responsible for handling the data collected from the Intel RealSense camera utilized to identify and locate the objects that our robot is tasked with blocking. It contains a CV bridge to enable OpenCV integration with ROS, subscribes to the RealSense's camera data, and ultimately publishes 3-dimensional coordinate data of the centroid of the object of interest (a red ball for our purposes).
In order to identify the ball, video frames are iteratively thresholded for a range of HSV values that closely match those of our ball. Once the area of interest is located, a contour is created around its edges and the centroid of the contour located. This centroid can then be treated as the location of the ball in the camera frame and published appropriately.
transforms
Knowing where the ball is relative to the camera is great, but it doesn't help the robot locate the ball. In order to accomplish this, transformations between the camera frame and the robot frame are necessary. This node subscribes to both the ball coordinates from the perception node and AprilTag detections, and publishes the transformed ball coordinates in the robot frame.
In order to complete the relationship between the two frames, an AprilTag with a known transformation between itself and the baselink of the robot (positioned on the floor next to the robot) was used. Using the RealSense, the transformation between the camera frame and the AprilTag can then also be determined. Using these three frames and their relationships, the transformation between coordinates in the camera frame and coordinates in the robot frame can finally be determined.
motion_control
This node provides the core functionality of the robokeeper. Primarily, it subscribes to the topic containing the ball coordinates in the robot frame and contains a number of services utilized to interact with its environment in several ways.
The main service used is /start_keeping. As the name suggests, this service allows the robot to begin interpreting the ball coordinates and attempting to intersect it at the goal line. Appropriate joint trajectory commands are sent to the robot through a mix of MoveIt! and direct joint publishing (depending on the service called) in order to accomplish the task. This node also keeps track of goals scored by determining if the ball has entered the net.
Services
-
The
resetservice moves the Adroit arm directly in front of its base and the goal.rosservice call /reset -
The
keepservice moves the robotic arm to a pose that is only dependent on a y-value. An example of the service being called follows.rosservice call /keep "pos: 0.0" -
above_paddleis a service that moves the arm directly above the paddle holster to get in a position for consistent retrieval.rosservice call /above_paddle -
To retrieve the paddle, the
retrieve_paddlecan be called. It moves the arm to a postion where it can grip the paddle, it then closes the gripper, and finally moves to the same position asabove_paddle.rosservice call /retrieve_paddle -
The
start_keepingservice enables the robot to block the red ball from entering the goal.rosservice call /start_keeping -
To stop the robot from moving and tracking the ball, call the
stop_keepingservice.rosservice call /stop_keeping
Additional Notes
There are some features within this code that were partially developed, but not completed due to time contraints. Because of this, you may notice certain things in the source code that are not mentioned here.
An example of this is the scoreboard feature. The original plan was to include both a goal counter and block counter when playing with the robot and display these stats to the user in order to create a game. The goal counter was successfully created, but we didn't have time to complete the black counter. The goal counter is located within the 'motion_control' node and the infrastructure for displaying the actual scoreboard using the 'tkinter' library is located in a node called 'scorekeeper'.