DiffAI v3 
DiffAI is a system for training neural networks to be provably robust and for proving that they are robust. The system was developed for the 2018 ICML paper and the 2019 ArXiV Paper.
Background
By now, it is well known that otherwise working networks can be tricked by clever attacks. For example Goodfellow et al. demonstrated a network with high classification accuracy which classified one image of a panda correctly, and a seemingly identical attack picture incorrectly. Many defenses against this type of attack have been produced, but very few produce networks for which provably verifying the safety of a prediction is feasible.
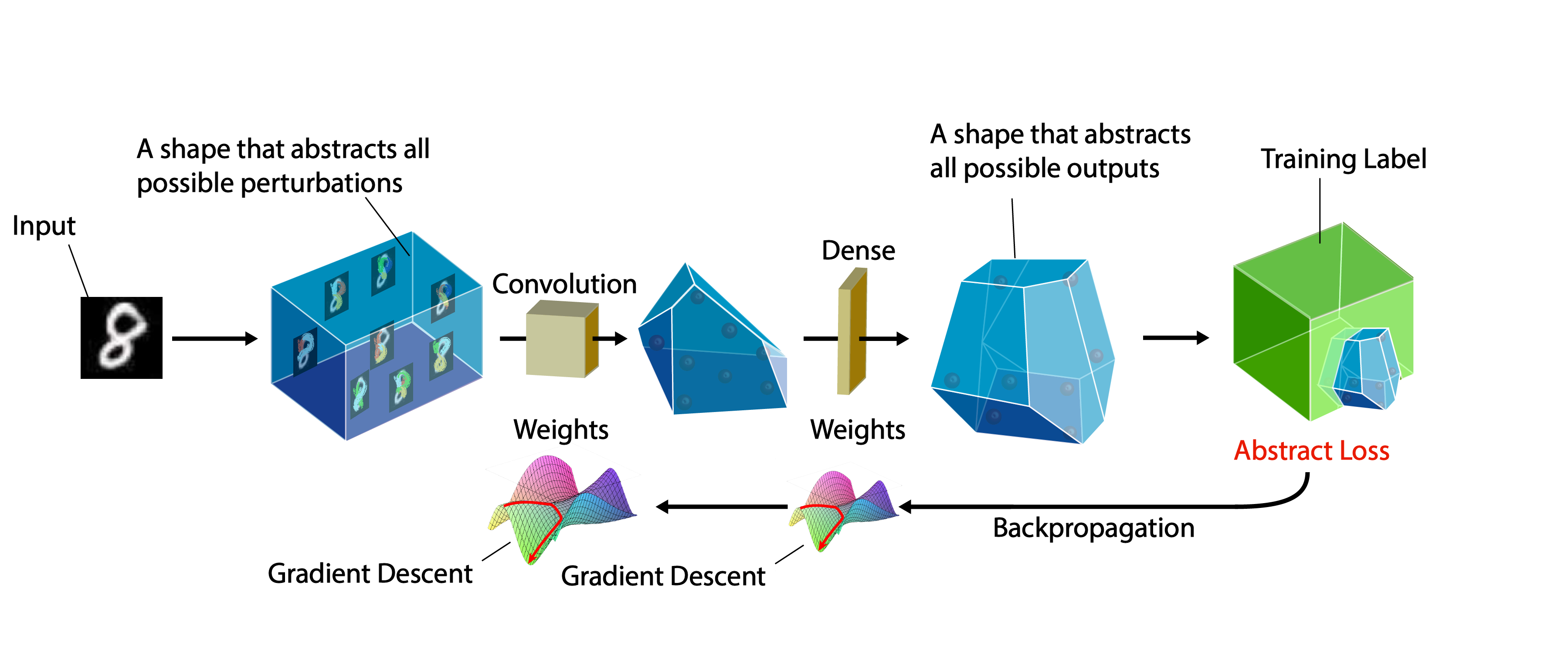
Abstract Interpretation is a technique for verifying properties of programs by soundly overapproximating their behavior. When applied to neural networks, an infinite set (a ball) of possible inputs is passed to an approximating "abstract" network to produce a superset of the possible outputs from the actual network. Provided an appropreate representation for these sets, demonstrating that the network classifies everything in the ball correctly becomes a simple task. The method used to represent these sets is the abstract domain, and the specific approximations are the abstract transformers.
In DiffAI, the entire abstract interpretation process is programmed using PyTorch so that it is differentiable and can be run on the GPU, and a loss function is crafted so that low values correspond to inputs which can be proved safe (robust).
Whats New In v3?
- Abstract Networks: one can now customize the handling of the domains on a per-layer basis.
- Training DSL: A DSL has been exposed to allow for custom training regimens with complex parameter scheduling.
- Cross Loss: The box goal now uses the cross entropy style loss by default as suggested by Gowal et al. 2019
- Conversion to Onyx: We can now export to the onyx format, and can export the abstract network itself to onyx (so that one can run abstract analysis or training using tensorflow for example).
Requirements
python 3.6.7, and virtualenv, torch 0.4.1.
Recommended Setup
$ git clone https://github.com/eth-sri/DiffAI.git
$ cd DiffAI
$ virtualenv pytorch --python python3.6
$ source pytorch/bin/activate
(pytorch) $ pip install -r requirements.txt
Note: you need to activate your virtualenv every time you start a new shell.
Getting Started
DiffAI can be run as a standalone program. To see a list of arguments, type
(pytorch) $ python . --help
At the minimum, DiffAI expects at least one domain to train with and one domain to test with, and a network with which to test. For example, to train with the Box domain, baseline training (Point) and test against the FGSM attack and the ZSwitch domain with a simple feed forward network on the MNIST dataset (default, if none provided), you would type:
(pytorch) $ python . -d "Point()" -d "Box()" -t "PGD()" -t "ZSwitch()" -n ffnn
Unless otherwise specified by "--out", the output is logged to the folder "out/".
In the folder corresponding to the experiment that has been run, one can find the saved configuration options in "config.txt", and a pickled net which is saved every 10 epochs (provided that testing is set to happen every 10th epoch).
To load a saved model, use "--test" as per the example:
(pytorch) $ alias test-diffai="python . -d Point --epochs 1 --dont-write --test-freq 1"
(pytorch) $ test-diffai -t Box --update-test-net-name convBig --test PATHTOSAVED_CONVBIG.pynet --width 0.1 --test-size 500 --test-batch-size 500
Note that "--update-test-net-name" will create a new model based on convBig and try to use the weights in the pickled PATHTOSAVED_CONVBIG.pynet to initialize that models weights. This is not always necessary, but is useful when the code for a model changes (in components) but does not effect the number or usage of weight, or when loading a model pickled by a cuda process into a cpu process.
The default specification type is the L_infinity Ball specified explicitly by "--spec boxSpec", which uses an epsilon specified by "--width"
The default specification type is the L_infinity Ball specified explicitly by "--spec boxSpec", which uses an epsilon specified by "--width"
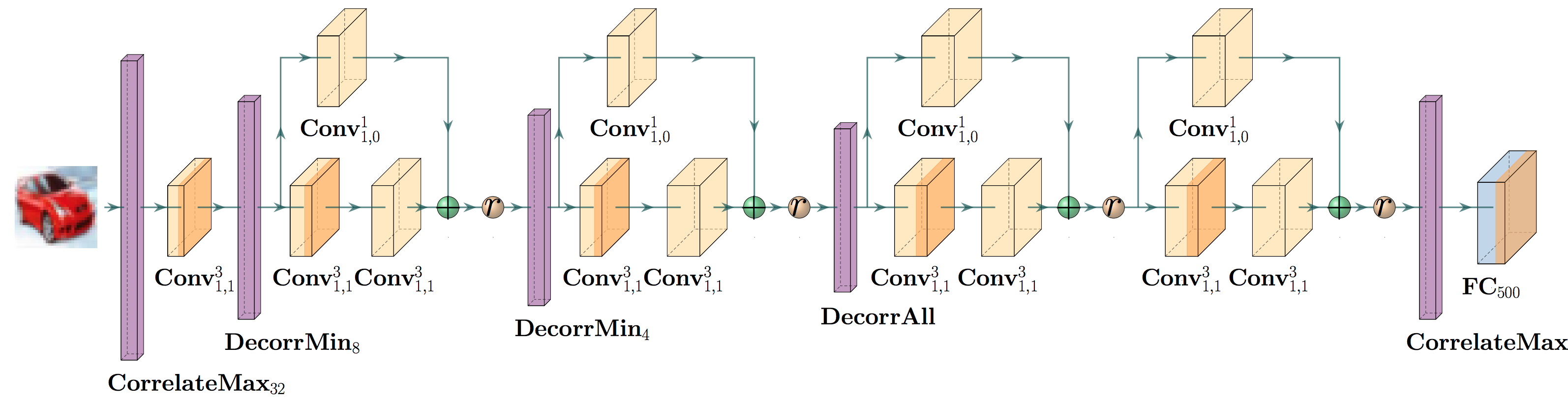
Abstract Networks
A cruical point of DiffAI v3 is that how a network is trained and abstracted should be part of the network description itself. In this release, we provide layers that allow one to alter how the abstraction works, in addition to providing a script for converting an abstract network to onyx so that the abstract analysis might be run in tensorflow. Below is a list of the abstract layers that we have included.
- CorrMaxPool3D
- CorrMaxPool2D
- CorrFix
- CorrMaxK
- CorrRand
- DecorrRand
- DecorrMin
- DeepLoss
- ToZono
- ToHZono
- Concretize
- CorrelateAll
Training Domain DSL
In DiffAI v3, a dsl has been provided to specify arbitrary training domains. In particular, it is now possible to train on combinations of attacks and abstract domains on specifications defined by attacks. Specifying training domains is possible in the command line using -d "DOMAIN_INITIALIZATION". The possible combinations are the classes listed in domains.py. The same syntax is also supported for testing domains, to allow for testing robustness with different epsilon-sized attacks and specifications.
Listed below are a few examples:
-
-t "IFGSM(k=4, w=0.1)" -t "ZNIPS(w=0.3)"Will first test with the PGD attack with an epsilon=w=0.1 and, the number of iterations k=4 and step size set to w/k. It will also test with the zonotope domain using the transformer specified in our NIPS 2018 paper with an epsilon=w=0.3. -
-t "PGD(r=3,k=16,restart=2, w=0.1)"tests on points found using PGD with a step size of r*w/k and two restarts, and an attack-generated specification. -
-d Point()is standard non-defensive training. -
-d "LinMix(a=IFGSM(), b=Box(), aw=1, bw=0.1)"trains on points produced by pgd with the default parameters listed in domains.py, and points produced using the box domain. The loss is combined linearly using the weights aw and bw and scaled by 1/(aw + bw). The epsilon used for both is the ambient epsilon specified with "--width". -
-d "DList((IFGSM(w=0.1),1), (Box(w=0.01),0.1), (Box(w=0.1),0.01))"is a generalization of the Mix domain allowing for training with arbitrarily many domains at once weighted by the given values (the resulting loss is scaled by the inverse of the sum of weights). -
-d "AdvDom(a=IFGSM(), b=Box())"trains using the Box domain, but constructs specifications as L∞ balls containing the PGD attack image and the original image "o". -
-d "BiAdv(a=IFGSM(), b=Box())"is similar, but creates specifications between the pgd attack image "a" and "o - (a - o)".
One domain we have found particularly useful for training is Mix(a=PGD(r=3,k=16,restart=2, w=0.1), b=BiAdv(a=IFGSM(k=5, w=0.05)), bw=0.1).
While the above domains are all deterministic (up to gpu error and shuffling orders), we have also implemented nondeterministic training domains:
-
-d "Coin(a=IFGSM(), b=Box(), aw=1, bw=0.1)"is like Mix, but chooses which domain to train a batch with by the probabilities determined by aw / (aw + bw) and bw / (aw + bw). -
-d "DProb((IFGSM(w=0.1),1), (Box(w=0.01),0.1), (Box(w=0.1),0.01))"is to Coin what DList is to Mix. -
-d AdvDom(a=IFGSM(), b=DList((PointB(),1), (PointA(), 1), (Box(), 0.2)))can be used to share attack images between multiple training types. Here an attack image "m" is found using PGD, then both the original image "o" and the attack image "m" are passed to DList which trains using three different ways: PointA trains with "o", PointB trains with "m", and Box trains on the box produced between them. This can also be used with Mix. -
-d Normal(w=0.3)trains using images sampled from a normal distribution around the provided image using standard deviation w. -
-d NormalAdv(a=IFGSM(), w=0.3)trains using PGD (but this could be an abstract domain) where perturbations are constrained to a box determined by a normal distribution around the original image with standard deviation w. -
-d InSamp(0.2, w=0.1)uses Inclusion sampling as defined in the ArXiv paper.
There are more domains implemented than listed here, and of course more interesting combinations are possible. Please look carefully at domains.py for default values and further options.
Parameter Scheduling DSL
In place of many constants, you can use the following scheduling devices.
-
Lin(s,e,t,i)Linearly interpolates between s and e over t epochs, using s for the first i epochs. -
Until(t,a,b)Uses a for the first t epochs, then switches to using b (telling b the current epoch starting from 0 at epoch t).
Suggested Training
LinMix(a=IFGSM(k=2), b=InSamp(Lin(0,1,150,10)), bw = Lin(0,0.5,150,10)) is a training goal that appears to work particularly well for CIFAR10 networks.
Contents
- components.py: A high level neural network library for composable layers and operations
- goals.py: The DSL for specifying training losses and domains, and attacks which can be used as a drop in replacement for pytorch tensors in any model built with components from components.py
- scheduling.py: The DSL for specifying parameter scheduling.
- models.py: A repository of models to train with which are used in the paper.
- convert.py: A utility for converting a model with a training or testing domain (goal) into an onyx network. This is useful for exporting DiffAI abstractions to tensorflow.
- __main__.py: The entry point to run the experiments.
- helpers.py: Assorted helper functions. Does some monkeypatching, so you might want to be careful importing our library into your project.
- AllExperimentsSerial.sh: A script which runs the training experiments from the 2019 ArXiv paper from table 4 and 5 and figure 5.
Notes
Not all of the datasets listed in the help message are supported. Supported datasets are:
- CIFAR10
- CIFAR100
- MNIST
- SVHN
- FashionMNIST
Unsupported datasets will not necessarily throw errors.
Results on Standard Networks
Download all defended networks, logs, and configs
MNIST
| Network | Number of Neurons | Number of Parameters | Number ReLU Layers |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFNN | 500 | 119910 | 5 |
| ConvSmall | 3604 | 89606 | 3 |
| ConvMed | 4804 | 166406 | 3 |
| ConvBig | 48064 | 1974762 | 6 |
| ConvLargeIBP | 175816 | 5426402 | 6 |
| TruncatedVGG | 151040 | 13109706 | 5 |
0.1
| Network | Standard Accuracy | MI_FGSM Accuracy | HBox Provability |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFNN | 93.3% | 90.8% | 88.9% |
| ConvSmall | 97.8% | 96.2% | 95.5% |
| ConvMed | 97.8% | 96.3% | 95.5% |
| ConvBig | 98.5% | 97.2% | 95.6% |
| ConvLargeIBP | 98.7% | 97.5% | 95.8% |
| TruncatedVGG | 98.9% | 97.7% | 95.6% |
0.3
| Network | Standard Accuracy | MI_FGSM Accuracy | HBox Provability |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFNN | 80.2% | 73.4% | 62.6% |
| ConvSmall | 96.9% | 93.6% | 89.1% |
| ConvMed | 96.6% | 93.1% | 89.3% |
| ConvBig | 97.0% | 95.2% | 87.8% |
| ConvLargeIBP | 97.2% | 95.4% | 88.8% |
| TruncatedVGG | 96.5% | 94.4% | 87.6% |
CIFAR10
| Network | Number of Neurons | Number of Parameters | Number ReLU Layers |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFNN | 500 | 348710 | 5 |
| ConvSmall | 4852 | 125318 | 3 |
| ConvMed | 6244 | 214918 | 3 |
| ConvBig | 62464 | 2466858 | 6 |
| ConvLargeIBP | 229576 | 6963554 | 6 |
| TruncatedVGG | 197120 | 17043018 | 5 |
2/255
| Network | Standard Accuracy | MI_FGSM Accuracy | HBox Provability |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFNN | 45.1% | 37.0% | 33.1% |
| ConvSmall | 56.1% | 46.2% | 42.4% |
| ConvMed | 56.9% | 46.6% | 43.2% |
| ConvBig | 61.9% | 51.4% | 45.0% |
| ConvLargeIBP | 61.1% | 51.4% | 44.5% |
| TruncatedVGG | 62.3% | 51.4% | 45.5% |
8/255
| Network | Standard Accuracy | MI_FGSM Accuracy | HBox Provability |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFNN | 33.5% | 23.8% | 19.0% |
| ConvSmall | 42.6% | 30.5% | 24.9% |
| ConvMed | 43.6% | 30.3% | 24.7% |
| ConvBig | 46.0% | 34.2% | 25.2% |
| ConvLargeIBP | 46.2% | 34.7% | 27.2% |
| TruncatedVGG | 45.9% | 34.4% | 27.0% |
Reproducing Results
All training runs from the paper can be reproduced as by the following command, in the same order as Table 6 in the appendix.
./AllExperimentsSerial.sh "-t MI_FGSM(k=20,r=2) -t HBox --test-size 10000 --test-batch-size 200 --test-freq 400 --save-freq 1 --epochs 420 --out all_experiments --write-first True --test-first False"
The training schemes can be written as follows (the names differ slightly from the presentation in the paper):
- Baseline: LinMix(a=Point(), b=Box(w=Lin(0,0.031373,150,10)), bw=Lin(0,0.5,150,10))
- InSamp: LinMix(a=Point(), b=InSamp(Lin(0,1,150,10)), bw=Lin(0,0.5, 150,10))
- InSampLPA: LinMix(a=Point(), b=InSamp(Lin(0,1,150,20), w=Lin(0,0.031373, 150, 20)), bw=Lin(0,0.5, 150, 20))
- Adv_{1}ISLPA: LinMix(a=IFGSM(w=Lin(0,0.031373,20,20), k=1), b=InSamp(Lin(0,1,150,10), w=Lin(0,0.031373,150,10)), bw=Lin(0,0.5,150,10))
- Adv_{3}ISLPA: LinMix(a=IFGSM(w=Lin(0,0.031373,20,20), k=3), b=InSamp(Lin(0,1,150,10), w=Lin(0,0.031373,150,10)), bw=Lin(0,0.5,150,10))
- Baseline_{18}: LinMix(a=Point(), b=InSamp(Lin(0,1,200,40)), bw=Lin(0,0.5,200,40))
- InSamp_{18}: LinMix(a=IFGSM(w=Lin(0,0.031373,20,20)), b=InSamp(Lin(0,1,200,40)), bw=Lin(0,0.5,200,40))
- Adv_{5}IS_{18}: LinMix(b=InSamp(Lin(0,1,200,40)), bw=Lin(0,0.5, 200, 40))
- BiAdv_L: LinMix(a=IFGSM(k=2), b=BiAdv(a=IFGSM(k=3, w=Lin(0,0.031373, 150, 30)), b=Box()), bw=Lin(0,0.6, 200, 30))
To test a saved network as in the paper, use the following command:
python . -D CIFAR10 -n ResNetLarge_LargeCombo -d Point --width 0.031373 --normalize-layer True --clip-norm False -t 'MI_FGSM(k=20,r=2)' -t HBox --test-size 10000 --test-batch-size 200 --epochs 1 --test NAMEOFSAVEDNET.pynet
Assorted
- DiffAI is now on version 3.0.
- This repository contains the code used for the experiments in the 2019 ArXiV Paper.
- To reproduce the experiments from the 2018 ICML paper Differentiable Abstract Interpretation for Provably Robust Neural Networks, one must download the source from download the source code for Version 1.0
- Further information and related projects can be found at the SafeAI Project
- High level slides
Citing This Framework
@inproceedings{
title={Differentiable Abstract Interpretation for Provably Robust Neural Networks},
author={Mirman, Matthew and Gehr, Timon and Vechev, Martin},
booktitle={International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML)},
year={2018},
url={https://www.icml.cc/Conferences/2018/Schedule?showEvent=2477},
}
Contributors
- Matthew Mirman - [email protected]
- Gagandeep Singh - [email protected]
- Timon Gehr - [email protected]
- Marc Fischer - [email protected]
- Martin Vechev - [email protected]
License and Copyright
- Copyright (c) 2018 Secure, Reliable, and Intelligent Systems Lab (SRI), ETH Zurich
- Licensed under the MIT License