百度网盘链接及提取码:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1HKpgakNx1hNlOuZJuW6T1w
提取码:wylx
一个垃圾分类项目带你玩转飞桨多个产品(1)
- 基于PaddleClas实现垃圾分类,导出inference模型并利用PaddleHub Serving进行服务化部署。
点击上方Fork可以运行本项目
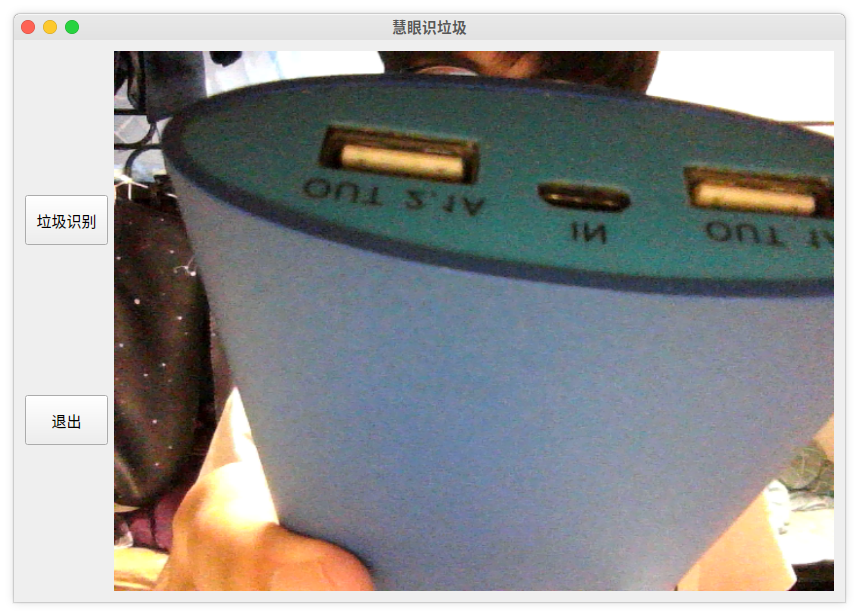
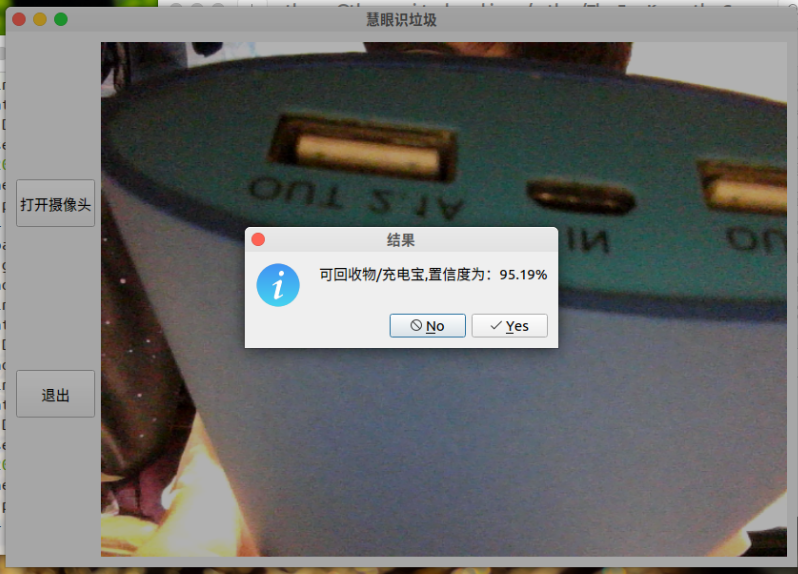
大家先看看效果哈
背景介绍
垃圾分类是对垃圾收集处置传统方式的改革,是对垃圾进行有效处置的一种科学管理方法。人们面对日益增长的垃圾产量和环境状况恶化的局面,如何通过垃圾分类管理,最大限度地实现垃圾资源利用,减少垃圾处置的数量,改善生存环境状态,是当前世界各国共同关注的迫切问题。
2019年6月25日,固体废物污染环境防治法修订草案初次提请全国人大常委会审议。草案对“生活垃圾污染环境的防治”进行了专章规定。2019年9月,为深入贯彻落实习近平总书记关于垃圾分类工作的重要指示精神,推动全国公共机构做好生活垃圾分类工作,国家机关事务管理局印发通知,公布《公共机构生活垃圾分类工作评价参考标准》,并就进一步推进有关工作提出要求。
就上海市而言,2019年1月31日《上海市生活垃圾管理条例》[1]获第十五届上海市人民代表大会通过,正式成为地方性法规,并于2019年7月1日起强制实施。此条例规定,个人或企业、单位混合投放垃圾将面临罚款等处罚。同年5月,上海市城市管理行政执法局出台《上海市生活垃圾分类违法行为查处规定》和《〈上海市生活垃圾管理条例〉行政处罚裁量基准》[2],对垃圾分类违法行为的行政处罚进行详细阐释。至此,申城成为全国第一个实行垃圾分类的城市。
此外,据新闻媒体报道,自2020年11月13日起,东华大学研究生新生入学教育新增一项“垃圾分类考试”。新生需回答垃圾分类相关知识的选择题,达到90分以上才能过关。而“高校研究生进行垃圾分类考试”再一次将“垃圾分类”推向高潮。
本项目利用PaddleClas图像分类套件进行垃圾分类开发,本项目使用 2019华为云AI大赛·垃圾分类数据集进行开发,总体效果具备较好的分类性能。
PaddleClas介绍
飞桨图像分类套件PaddleClas是飞桨为工业界和学术界所准备的一个图像分类任务的工具集,助力使用者训练出更好的视觉模型和应用落地。PaddleClas 是百度基于PaddlePaddle框架推出的图像分类开发套件,实现了23个系列丰富的分类模型,多种数据增广方式,SSLD知识蒸馏高阶优化方案,并可以很方便的对训练出的模型进行工业级部署。特性:
-
丰富的模型库:基于ImageNet1k分类数据集,PaddleClas提供了29个系列的分类网络结构和训练配置,133个预训练模型和性能评估。
-
SSLD知识蒸馏:基于该方案蒸馏模型的识别准确率普遍提升3%以上。
-
数据增广:支持AutoAugment、Cutout、Cutmix等8种数据增广算法详细介绍、代码复现和在统一实验环境下的效果评估。
-
10万类图像分类预训练模型:百度自研并开源了基于10万类数据集训练的
ResNet50_vd模型,在一些实际场景中,使用该预训练模型的识别准确率最多可以提升30%。 -
多种训练方案,包括多机训练、混合精度训练等。
-
多种预测推理、部署方案,包括TensorRT预测、Paddle-Lite预测、模型服务化部署、模型量化、Paddle Hub等。
-
可运行于Linux、Windows、MacOS等多种系统。
# 解压数据集
!rar x data/data43905/garbage.rar The-Eye-Konws-the-Garbage
我们观察garbage文件目录,其中需要特别注意的是:
- garbage_classify_rule.json 存放着标签与具体垃圾的对应关系
- labels.txt 存放着所有标签
- train.txt 存放着训练集内图片的相对地址与对应标签(例:./29/img_14678.jpg 29)
- validate.txt 存放着验证集内图片的相对地址与对应标签(例:./0/img_18.jpg 0)
本数据集符合ImageNet格式,故在此基础上使用PaddleClas极其便利!
模型选取
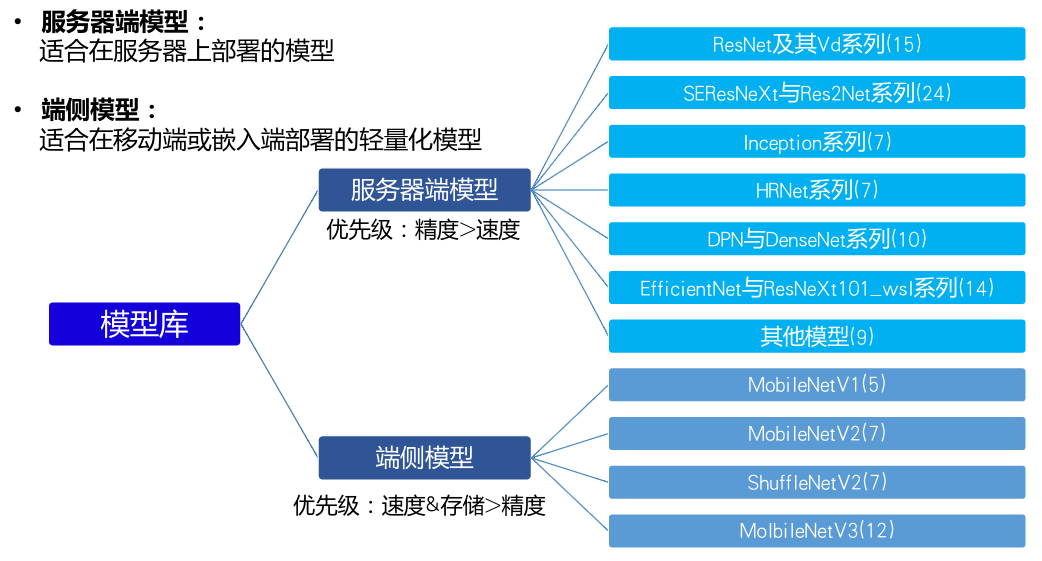
数据集准备好后,接下来就是在PaddleClas提供的23个系列的模型中选择一个较为合适本项目的模型。
由图可知,模型主要分为两类:服务器端模型和移动端模型。移动端模型以轻量化为主要设计目标,通常速度快体积小,因此会牺牲一定的精度。而服务器端模型的精度通常很高,然其体积也相对较大。基于本项目实地应用场景,我们在这个项目中选择服务器端模型,并最终选择了ResNet_Vd。ResNet_Vd是PaddleClas框架主推的模型,经过了大量精度和速度上的优化。如果在自己的项目中不是很清楚如何选择模型,从ResNet_Vd开始尝试是一个不错的选择。而由于本项目的数据集还不是特别大,故结合RandomErasing的数据增广方式进行训练可以在原有基础上进一步提升精度。
模型训练
下面就到了关键的模型训练时刻!使用PaddleClas训练模型基本就是编写config文件。由于PaddleClas很贴心地为开发者提供了一份demo config文件,故而我们可以在此基础上进行修改。下面笔者将着重介绍几个关键修改处:
- |classes_num |分类数|
- |total_images|总图片数|
- | epochs |训练总epoch数|
- | file_list |标注训练集/验证集图片地址及其标签的txt文件地址|
- |data_dir|数据集目录|
配置完config文件后即可正式开始模型训练,一般来说PaddleClas的模型训练是基于tools.py命令行进行的,命令行启动代码如下:
!python3 train.py -c ResNet50_vd_ssld_random_erasing_finetune.yaml
本项目中训练了60个epoch,大约在第42个epoch处会得到最佳模型。
%cd /home/aistudio/The-Eye-Konws-the-Garbage/
!python3 train.py -c ResNet50_vd_ssld_random_erasing_finetune.yaml
模型导出
训练出满意的模型后我们会希望用训练得到的模型进行前向推理,这需要用到训练过程中保存的权重文件。PaddlePaddle框架保存的权重文件分为两种:支持前向推理和反向梯度的训练模型 和 只支持前向推理的推理模型。二者的区别是推理模型针对推理速度和显存做了优化,裁剪了一些只在训练过程中才需要的tensor,降低显存占用,并进行了一些类似层融合,kernel选择的速度优化。PaddleClas在训练过程中保存的模型属于训练模型,默认保存在 ./output/模型结构 路径下。
接下来我们通过PaddleClas中提供的模型转换脚本将训练模型转换为推理模型。
# 将PaddleClas的模型转换为inference模型
%cd /home/aistudio/The-Eye-Konws-the-Garbage/
!python export_model.py \
--model ResNet50_vd \
--pretrained_model ./output/ResNet50_vd/best_model/ppcls \
--output_path ./inference \
--class_dim 40
&emsp执行完毕后我们可以看到转换之后在./inference中生成了两个文件,model是模型结构,params是模型权重。转换完毕,最后一步是进行推理。推理的输入图片可以从 数据集文件夹中任意选择,填入对应的路径即可。
# 执行预测
%cd The-Eye-Konws-the-Garbage
!python predict.py \
--image_file "./garbage/0/img_210.jpg" \
--model_file "./inference/inference.pdmodel" \
--params_file "./inference/inference.pdiparams" \
--use_gpu=False \
--use_tensorrt=False
基于PaddleHub Serving的服务部署
首先需要在params.py中查看和修改推理模型路径,即如下图所示: 然后需要安装服务模块,具体代码如下: hub install The-Eye-Konws-the-Garbage
# 安装服务模块
%cd /home/aistudio/
!hub install The-Eye-Konws-the-Garbage/
当我们安装完服务模块后,我们便可以启动配置文件,官方提供了两种启动方式:
方式1. 命令行命令启动(仅支持CPU) 启动命令:
$ hub serving start --modules Module1==Version1 \
--port XXXX \
--use_multiprocess \
--workers \
参数:
| 参数 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| --modules/-m | [必选] PaddleHub Serving预安装模型,以多个Module==Version键值对的形式列出当不指定Version时,默认选择最新版本 |
| --port/-p | [可选] 服务端口,默认为8866 |
| --use_multiprocess | [可选] 是否启用并发方式,默认为单进程方式,推荐多核CPU机器使用此方式Windows操作系统只支持单进程方式 |
| --workers | [可选] 在并发方式下指定的并发任务数,默认为2*cpu_count-1,其中cpu_count为CPU核数 |
如按默认参数启动服务: hub serving start -m garbage_classification
这样就完成了一个服务化API的部署,使用默认端口号8866。
方式2. 配置文件启动(支持CPU、GPU)
启动命令:
hub serving start -c config.json
其中,config.json格式如下:
{
"modules_info": {
"garbage_classification": {
"init_args": {
"version": "1.0.0",
"use_gpu": true,
"enable_mkldnn": false
},
"predict_args": {
}
}
},
"port": 8866,
"use_multiprocess": false,
"workers": 2
}
init_args中的可配参数与module.py中的_initialize函数接口一致。其中,- 当
use_gpu为true时,表示使用GPU启动服务。 - 当
enable_mkldnn为true时,表示使用MKL-DNN加速。
- 当
predict_args中的可配参数与module.py中的predict函数接口一致。
注意:
- 使用配置文件启动服务时,其他参数会被忽略。
- 如果使用GPU预测(即,
use_gpu置为true),则需要在启动服务之前,设置CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES环境变量,如:export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,否则不用设置。 use_gpu不可与use_multiprocess同时为true。use_gpu与enable_mkldnn同时为true时,将忽略enable_mkldnn,而使用GPU。
如,使用GPU 3号卡启动串联服务:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=3
hub serving start -c config.json
# 命令行启动
%cd /home/aistudio/The-Eye-Konws-the-Garbage/
!hub serving start -m garbage_classification
配置好服务端后,可使用以下命令发送预测请求,获取预测结果:
%cd /home/aistudio/The-Eye-Konws-the-Garbage
!python test.py
项目部署
随后我们进行项目的具体部署,具体细节此处我们不予细讲,读者可在本地跑通后执行如下命令:python The-Eye-Konws-the-Garbage/garbage_end_side.py
相关效果如开头处所示
总结与反思
- 本项目总体使用PaddleClas实现了垃圾分类,并取得了较好的预测效果。
- 本项目基于PaddleHub Serving 实现了服务部署。
- 本项目后绪将结合PaddleHub增加语音播报功能,提高用户体验。
个人相关介绍
-
笔名:左右
-
华东理工大学自动化专业大二在读
-
号称:冷板凳常客
-
热衷于利用人工智能技术做点有价值的东西,为社会做点小事情;
-
另外也研究点多智能体
-
偶尔写点随笔、摄影、仰望星空...