Development Kit for MIT Scene Parsing Benchmark
[NEW!] Our PyTorch implementation is released in the following repository:
https://github.com/hangzhaomit/semantic-segmentation-pytorch
Introduction
Table of contents:
- Overview of scene parsing benchmark
- Benchmark details
- Image list and annotations
- Submission format
- Evaluation routines
- Pretrained models
Please open an issue for questions, comments, and bug reports.
Overview of Scene Parsing Benchmark
The goal of this benchmark is to segment and parse an image into different image regions associated with semantic categories, such as sky, road, person, and bed. It is similar to semantic segmentation tasks in COCO and Pascal Dataset, but the data is more scene-centric and with a diverse range of object categories. The data for this benchmark comes from ADE20K Dataset (the full dataset will be released after the benchmark) which contains more than 20K scene-centric images exhaustively annotated with objects and object parts. Specifically, the benchmark data is divided into 20K images for training, 2K images for validation, and another batch of held-out images for testing. There are in total 150 semantic categories included in the benchmark for evaluation, which include stuffs like sky, road, grass, and discrete objects like person, car, bed. Note that non-uniform distribution of objects occurs in the images, mimicking a more natural object occurrence in daily scenes.
The webpage of the benchmark is at http://sceneparsing.csail.mit.edu. You could download the data at the webpage.
Benchmark details
Data
There are three types of data, the training, the validation and the testing. The training data contains 20210 images, the validation data contains 2000 images. The testing data contains 2000 images which will be released in middle August. Each image in the training data and validation data has an annotation mask, indicating the labels for each pixel in the image.
After untarring the data file (please download it from http://sceneparsing.csail.mit.edu), the directory structure should be similar to the following,
the training images:
images/training/ADE_train_00000001.jpg
images/training/ADE_train_00000002.jpg
...
images/training/ADE_train_00020210.jpg
the corresponding annotation masks for the training images:
annotations/training/ADE_train_00000001.png
annotations/training/ADE_train_00000002.png
...
annotations/training/ADE_train_00020210.png
the validation images:
images/validation/ADE_val_00000001.jpg
images/validation/ADE_val_00000002.jpg
...
images/validation/ADE_val_00002000.jpg
the corresponding annotation masks for the validation images:
annotations/validation/ADE_val_00000001.png
annotations/validation/ADE_val_00000002.png
...
annotations/validation/ADE_val_00002000.png
the testing images will be released in a separate file in the middle Auguest. The directory structure will be: images/testing/ADE_test_00000001.jpg ...
Note: annotations masks contain labels ranging from 0 to 150, where 0 refers to "other objects". We do not consider those pixels in our evaluation.
objectInfo150.txt contains the information about the labels of the 150 semantic categories, including indices, pixel ratios and names.
Submission format to the evaluation server
To evaluate the algorithm on the test set of the benchmark (link: http://sceneparsing.csail.mit.edu/eval/), participants are required to upload a zip file which contains the predicted annotation mask for the given testing images to the evaluation server. The naming of the predicted annotation mask should be the same as the name of the testing images, while the filename extension should be png instead of jpg. For example, the predicted annotation mask for file ADE_test_00000001.jpg should be ADE_test_00000001.png.
Participants should check the zip file to make sure it could be decompressed correctly.
Interclass similarity
Some of the semantic classes in this dataset show some level of visual and semantic similarities across them. In order to quantify such similarities we include a matrix in human_semantic_similarity.mat, which includes human-perceived similarities between the 150 categories and can be used to train the segmentation models. In demoSimilarity.m, we show how to use that file.
Evaluation routines
The performance of the segmentation algorithms will be evaluated by the mean of (1) pixel-wise accuracy over all the labeled pixels, and (2) IoU (intersection over union) avereaged over all the 150 semantic categories.
Intersection over Union = (true positives) / (true positives + false positives + false negatives)
Pixel-wise Accuracy = correctly classifield pixels / labeled pixels
Final score = (Pixel-wise Accuracy + mean(Intersection over Union)) / 2
Demo code
In demoEvaluation.m, we have included our implementation of the standard evaluation metrics (pixel-wise accuracy and IoU) for the benchmark. As mentioned before, we ignore pixels labeled with 0's.
Please change the paths at the begining of the code accordingly to evalutate your own results. While running it correctly, you are expected to see output similar to:
Mean IoU over 150 classes: 0.1000
Pixel-wise Accuracy: 100.00%
In this case, we will take (0.1+1.0)/2=0.55 as your final score.
We have also provided demoVisualization.m, which helps you to visualize individual image results.
Training code
We provide the training code for three popular frameworks, Caffe, Torch7 and PyTorch (https://github.com/CSAILVision/sceneparsing/tree/master/trainingCode). You might need to modify the paths, and the data loader code accordingly to have all the things running on your own computer.
Pre-trained models
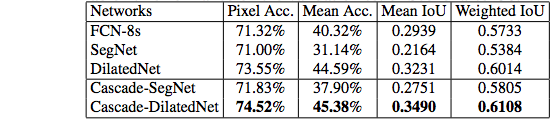
We release the pre-trained models for scene parsing at (http://sceneparsing.csail.mit.edu/model/). The demo code along with the model download links is at (https://github.com/CSAILVision/sceneparsing/blob/master/demoSegmentation.m). The models can be used for research only. The detail of how the models are trained is in the reference below. The performance of the models on the validation set of MIT SceneParse150 is as follows,
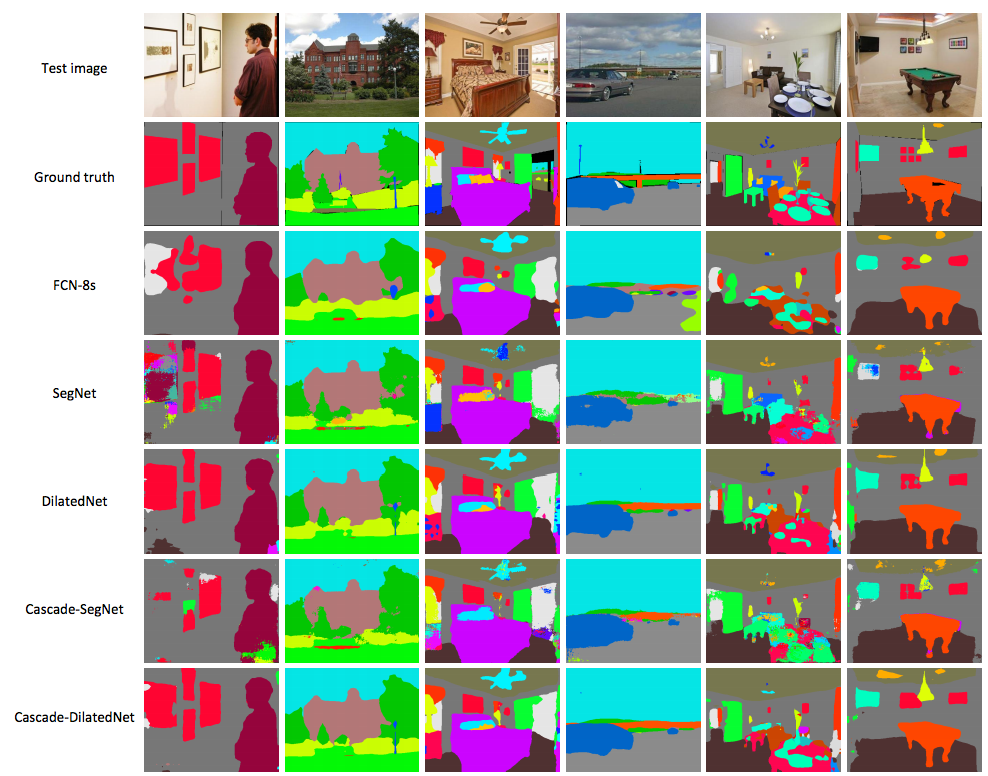
The qualitative results of the models are below:
Reference
If you find this scene parse benchmark or the data or the pre-trained models useful, please cite the following paper:
Scene Parsing through ADE20K Dataset. B. Zhou, H. Zhao, X. Puig, S. Fidler, A. Barriuso and A. Torralba. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017. (http://people.csail.mit.edu/bzhou/publication/scene-parse-camera-ready.pdf)
@inproceedings{zhou2017scene,
title={Scene Parsing through ADE20K Dataset},
author={Zhou, Bolei and Zhao, Hang and Puig, Xavier and Fidler, Sanja and Barriuso, Adela and Torralba, Antonio},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
year={2017}
}
Semantic Understanding of Scenes through ADE20K Dataset. B. Zhou, H. Zhao, X. Puig, S. Fidler, A. Barriuso and A. Torralba. arXiv:1608.05442. (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.05442.pdf)
@article{zhou2016semantic,
title={Semantic understanding of scenes through the ade20k dataset},
author={Zhou, Bolei and Zhao, Hang and Puig, Xavier and Fidler, Sanja and Barriuso, Adela and Torralba, Antonio},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.05442},
year={2016}
}