NeuralQA: A Usable Library for (Extractive) Question Answering on Large Datasets with BERT
Still in alpha, lots of changes anticipated. View demo on neuralqa.fastforwardlabs.com.
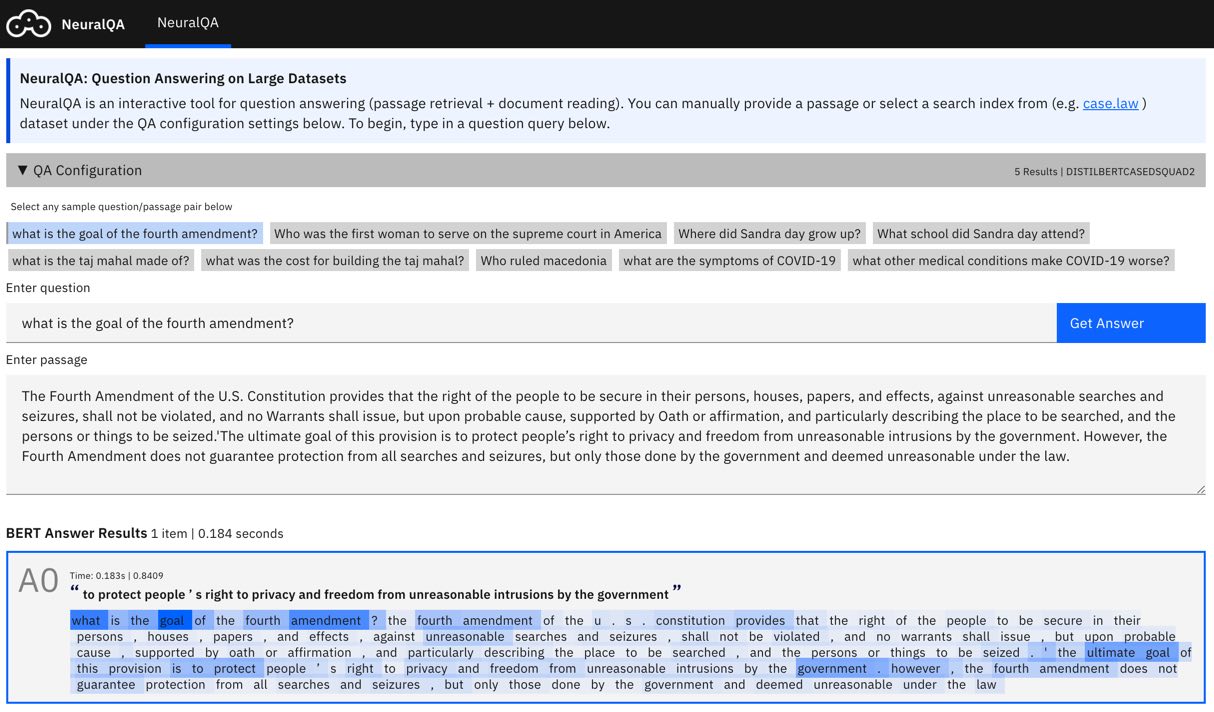
NeuralQA provides an easy to use api and visual interface for Extractive Question Answering (QA), on large datasets. The QA process is comprised of two main stages - Passage retrieval (Retriever) is implemented using ElasticSearch and Document Reading (Reader) is implemented using pretrained BERT models via the Huggingface Transformers api.
Usage
pip3 install neuralqa
Create (or navigate to) a folder you would like to use with NeuralQA. Run the following command line instruction within that folder.
neuralqa ui --port 4000
navigate to http://localhost:4000/#/ to view the NeuralQA interface. Learn about other command line options in the documentation here or how to configure NeuralQA to use your own reader models or retriever instances.
Note: To use NeuralQA with a retriever such as ElasticSearch, follow the instructions here to download, install, and launch a local elasticsearch instance and add it to your config.yaml file.
How Does it Work?
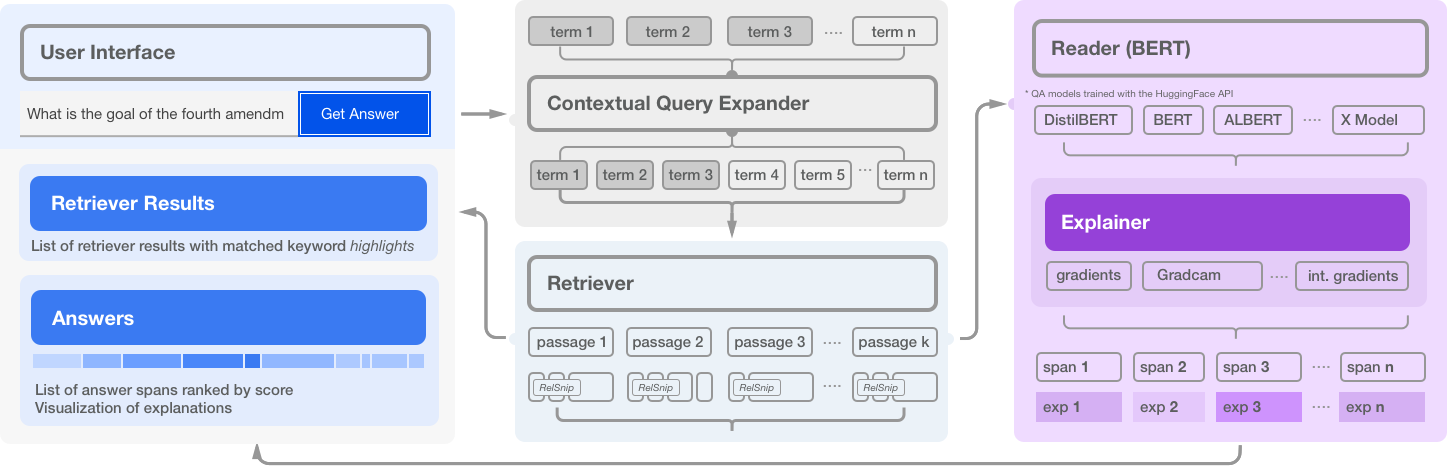
NeuralQA is comprised of several high level modules:
-
Retriever: For each search query (question), scan an index (elasticsearch), and retrieve a list of candidate matched passages.
-
Reader: For each retrieved passage, a BERT based model predicts a span that contains the answer to the question. In practice, retrieved passages may be lengthy and BERT based models can process a maximum of 512 tokens at a time. NeuralQA handles this in two ways. Lengthy passages are chunked into smaller sections with a configurable stride. Secondly, NeuralQA offers the option of extracting a subset of relevant snippets (RelSnip) which a BERT reader can then scan to find answers. Relevant snippets are portions of the retrieved document that contain exact match results for the search query.
-
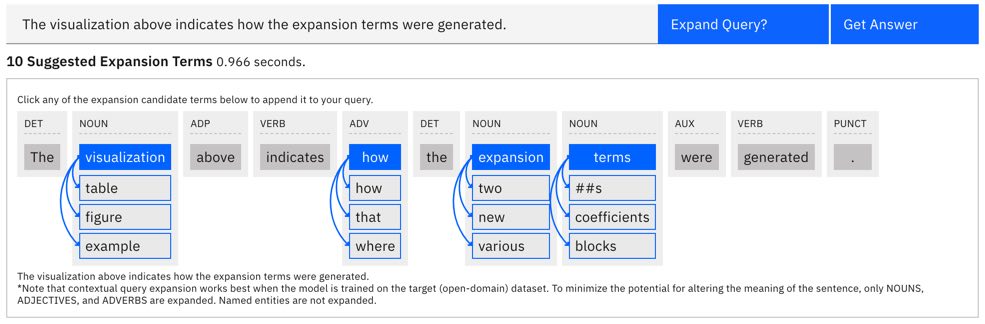
Expander: Methods for generating additional (relevant) query terms to improve recall. Currently, we implement Contextual Query Expansion using finetuned Masked Language Models. This is implemented via a user in the loop flow where the user can choose to include any suggested expansion terms.
- User Interface: NeuralQA provides a visual user interface for performing queries (manual queries where question and context are provided as well as queries over a search index), viewing results and also sensemaking of results (reranking of passages based on answer scores, highlighting keyword match, model explanations).
Configuration
Properties of modules within NeuralQA (ui, retriever, reader, expander) can be specified via a yaml configuration file. When you launch the ui, you can specify the path to your config file --config-path. If this is not provided, NeuralQA will search for a config.yaml in the current folder or create a default copy) in the current folder. Sample configuration shown below:
ui:
queryview:
intro:
title: "NeuralQA: Question Answering on Large Datasets"
subtitle: "Subtitle of your choice"
views: # select sections of the ui to hide or show
intro: True
advanced: True
samples: False
passages: True
explanations: True
allanswers: True
options: # values for advanced options
stride: ..
maxpassages: ..
highlightspan: ..
header: # header tile for ui
appname: NeuralQA
appdescription: Question Answering on Large Datasets
reader:
title: Reader
selected: twmkn9/distilbert-base-uncased-squad2
options:
- name: DistilBERT SQUAD2
value: twmkn9/distilbert-base-uncased-squad2
type: distilbert
- name: BERT SQUAD2
value: deepset/bert-base-cased-squad2
type: bert
Documentation
An attempt is being made to better document NeuralQA here - https://victordibia.github.io/neuralqa/.
Citation
A paper introducing NeuralQA and its components can be found here.
@article{dibia2020neuralqa,
title={NeuralQA: A Usable Library for Question Answering (Contextual Query Expansion + BERT) on Large Datasets},
author={Victor Dibia},
year={2020},
journal={Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP): System Demonstrations}
}