ViT Tensorflow
This repository contains the tensorflow implementation of the state-of-the-art vision transformers (a category of computer vision models first introduced in An Image is worth 16 x 16 words). This repository is inspired from the work of lucidrains which is vit-pytorch. I hope you enjoy these implementations :)
Models
- Vision Transformer: An Image is worth 16 x 16 words
- Convolutional Vision Transformer
- Pyramid Vision Transformer V1
- Pyramid Vision Transformer V2
- DeiT: Training Data Efficient Image Transforemrs & Distillation Through Attention
Requirements
pip install tensorflow
Vision Transformer
Vision transformer was introduced in An Image is worth 16 x 16 words. This model uses a Transformer encoder to classify images with pure attention and no convolution.
Usage
Defining the Model
from vit import ViT
import tensorflow as tf
vitClassifier = ViT(
num_classes=1000,
patch_size=16,
num_of_patches=(224//16)**2,
d_model=128,
heads=2,
num_layers=4,
mlp_rate=2,
dropout_rate=0.1,
prediction_dropout=0.3,
)
Params
num_classes: int
number of classes used for the final classification headpatch_size: int
patch_size used for the tokenizationnum_of_patches: int
number of patches after the tokenization which is used for the positional encoding, Generally it can be computed by the following formula(((h-patch_size)//patch_size) + 1)*(((w-patch_size)//patch_size) + 1)wherehis the height of the image andwis the width of the image. In addition, when height and width of the image are devisable by thepatch_sizethe following formula can be used as well(h//patch_size)*(w//patch_size)d_model: int
hidden dimension of the transformer encoder and the demnesion used for patch embeddingheads: int
number of heads used for the multi-head attention mechanismnum_layers: int
number of blocks in encoder transformermlp_rate: int
the rate of expansion in the feed-forward block of each transformer block (the dimension after expansion ismlp_rate * d_model)dropout_rate: float
dropout rate used in the multi-head attention mechanismprediction_dropout: float
dropout rate used in the final prediction head of the model
Inference
sampleInput = tf.random.normal(shape=(1 , 224 , 224 , 3))
output = vitClassifier(sampleInput , training=False)
print(output.shape) # (1 , 1000)
Training
vitClassifier.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
metrics=[
tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name="accuracy"),
tf.keras.metrics.SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy(k=5 , name="top_5_accuracy"),
])
vitClassifier.fit(
trainingData, #Tensorflow dataset of images and labels in shape of ((b , h , w , 3) , (b,))
validation_data=valData, #The same as training
epochs=100,)
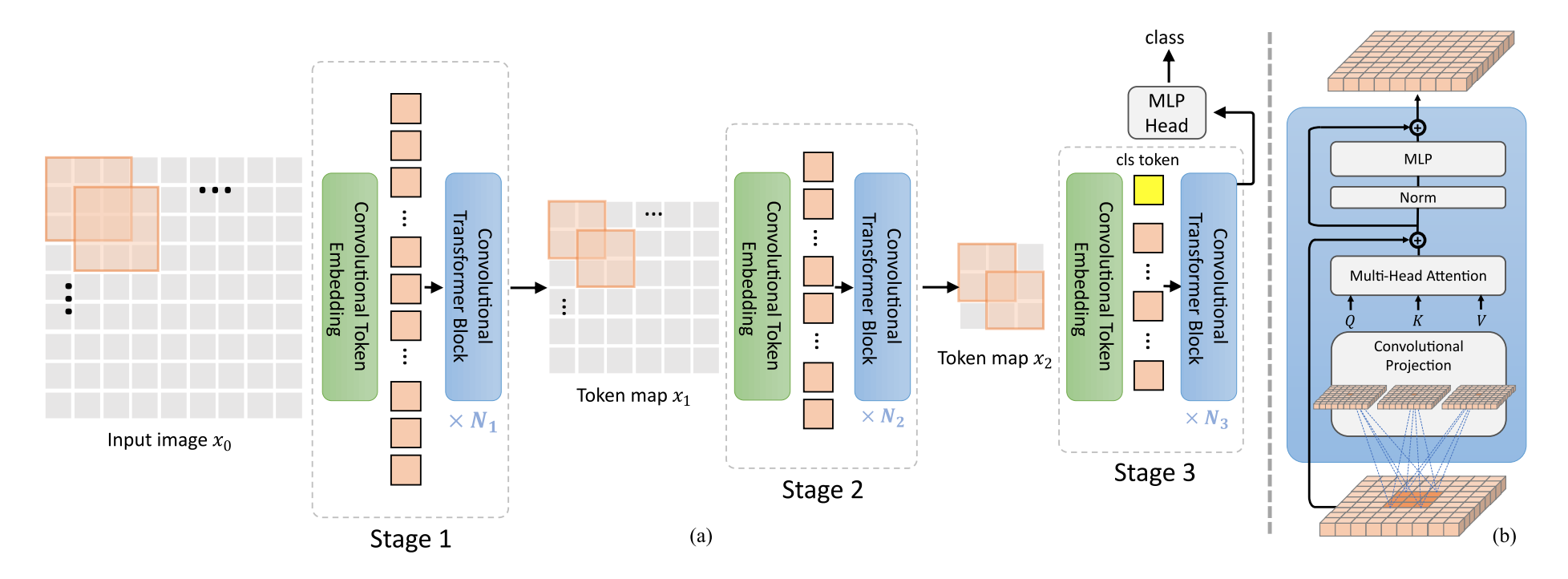
Convolutional Vision Transformer
Convolutional Vision Transformer was introduced in here. This model uses a hierarchical (multi-stage) architecture with convolutional embeddings in the begining of each stage. it also uses Convolutional Transformer Blocks to improve the orginal vision transformer by adding CNNs inductive bias into the architecture.
Usage
Defining the Model
from cvt import CvT , CvTStage
import tensorflow as tf
cvtModel = CvT(
num_of_classes=1000,
stages=[
CvTStage(projectionDim=64,
heads=1,
embeddingWindowSize=(7 , 7),
embeddingStrides=(4 , 4),
layers=1,
projectionWindowSize=(3 , 3),
projectionStrides=(2 , 2),
ffnRate=4,
dropoutRate=0.1),
CvTStage(projectionDim=192,
heads=3,
embeddingWindowSize=(3 , 3),
embeddingStrides=(2 , 2),
layers=1,
projectionWindowSize=(3 , 3),
projectionStrides=(2 , 2),
ffnRate=4,
dropoutRate=0.1),
CvTStage(projectionDim=384,
heads=6,
embeddingWindowSize=(3 , 3),
embeddingStrides=(2 , 2),
layers=1,
projectionWindowSize=(3 , 3),
projectionStrides=(2 , 2),
ffnRate=4,
dropoutRate=0.1)
],
dropout=0.5)
CvT Params
num_of_classes: int
number of classes used in the final prediction layerstages: list of CvTStage
list of cvt stagesdropout: float
dropout rate used for the prediction head
CvTStage Params
projectionDim: int
dimension used for the multi-head attention mechanism and the convolutional embeddingheads: int
number of heads in the multi-head attention mechanismembeddingWindowSize: tuple(int , int)
window size used for the convolutional emebddingembeddingStrides: tuple(int , int)
strides used for the convolutional embeddinglayers: int
number of convolutional transformer blocksprojectionWindowSize: tuple(int , int)
window size used for the convolutional projection in each convolutional transformer blockprojectionStrides: tuple(int , int)
strides used for the convolutional projection in each convolutional transformer blockffnRate: int
expansion rate of the mlp block in each convolutional transformer blockdropoutRate: float
dropout rate used in each convolutional transformer block
Inference
sampleInput = tf.random.normal(shape=(1 , 224 , 224 , 3))
output = cvtModel(sampleInput , training=False)
print(output.shape) # (1 , 1000)
Training
cvtModel.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
metrics=[
tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name="accuracy"),
tf.keras.metrics.SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy(k=5 , name="top_5_accuracy"),
])
cvtModel.fit(
trainingData, #Tensorflow dataset of images and labels in shape of ((b , h , w , 3) , (b,))
validation_data=valData, #The same as training
epochs=100,)
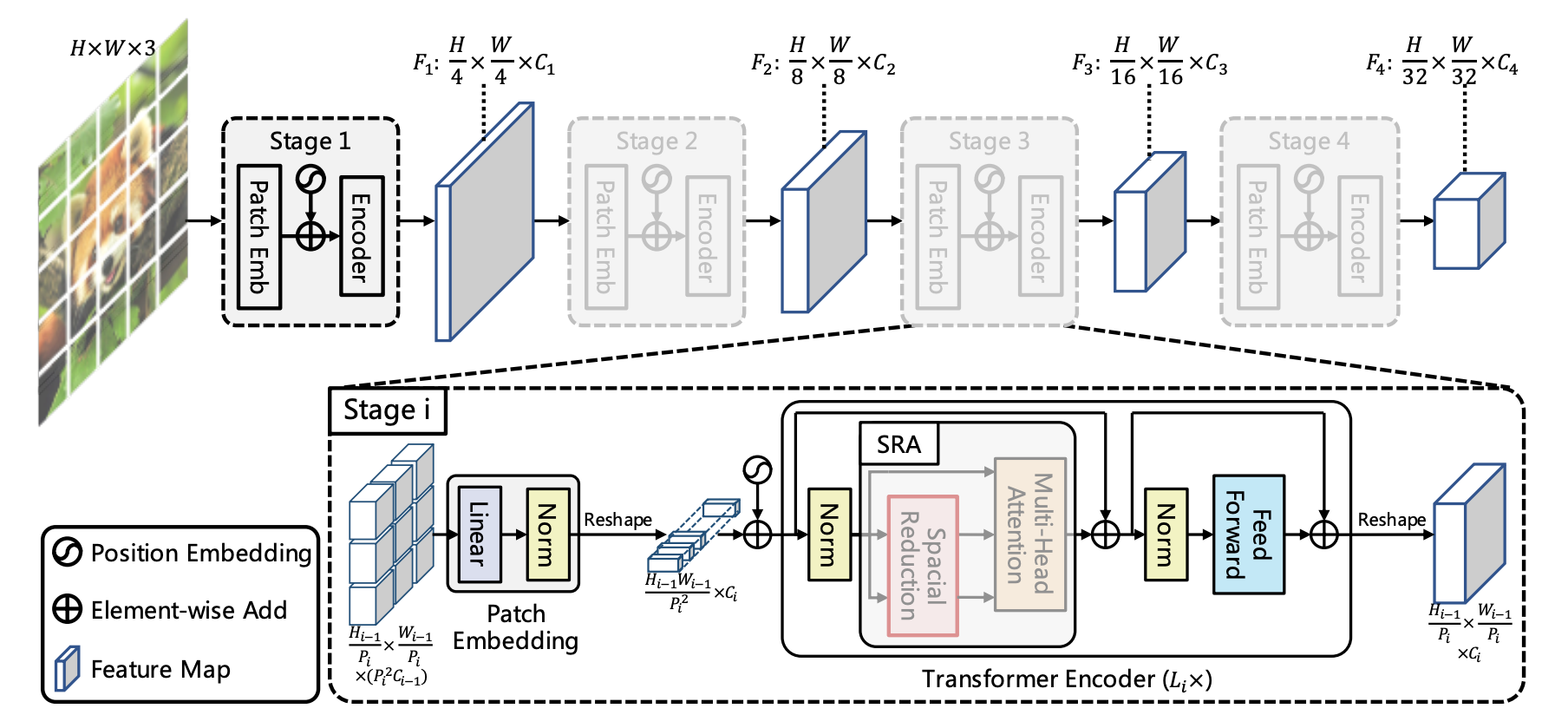
Pyramid Vision Transformer V1
Pyramid Vision Transformer V1 was introduced in here. This model stacks multiple Transformer Encoders to form the first convolution-free multi-scale backbone for various visual tasks including Image Segmentation , Object Detection and etc. In addition to this a new attention mechanism called Spatial Reduction Attention (SRA) is also introduced in this paper to reduce the quadratic complexity of the multi-head attention mechansim.
Usage
Defining the Model
from pvt_v1 import PVT , PVTStage
import tensorflow as tf
pvtModel = PVT(
num_of_classes=1000,
stages=[
PVTStage(d_model=64,
patch_size=(2 , 2),
heads=1,
reductionFactor=2,
mlp_rate=2,
layers=2,
dropout_rate=0.1),
PVTStage(d_model=128,
patch_size=(2 , 2),
heads=2,
reductionFactor=2,
mlp_rate=2,
layers=2,
dropout_rate=0.1),
PVTStage(d_model=320,
patch_size=(2 , 2),
heads=5,
reductionFactor=2,
mlp_rate=2,
layers=2,
dropout_rate=0.1),
],
dropout=0.5)
PVT Params
num_of_classes: int
number of classes used in the final prediction layerstages: list of PVTStage
list of pvt stagesdropout: float
dropout rate used for the prediction head
PVTStage Params
d_model: int
dimension used for theSRAmechanism and the patch embeddingpatch_size: tuple(int , int)
window size used for the patch emebddingheads: int
number of heads in theSRAmechanismreductionFactor: int
reduction factor used for the down sampling of theKandVin theSRAmechanismmlp_rate: int
expansion rate used in the feed-forward blocklayers: int
number of transformer encodersdropout_rate: float
dropout rate used in each transformer encoder
Inference
sampleInput = tf.random.normal(shape=(1 , 224 , 224 , 3))
output = pvtModel(sampleInput , training=False)
print(output.shape) # (1 , 1000)
Training
pvtModel.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
metrics=[
tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name="accuracy"),
tf.keras.metrics.SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy(k=5 , name="top_5_accuracy"),
])
pvtModel.fit(
trainingData, #Tensorflow dataset of images and labels in shape of ((b , h , w , 3) , (b,))
validation_data=valData, #The same as training
epochs=100,)
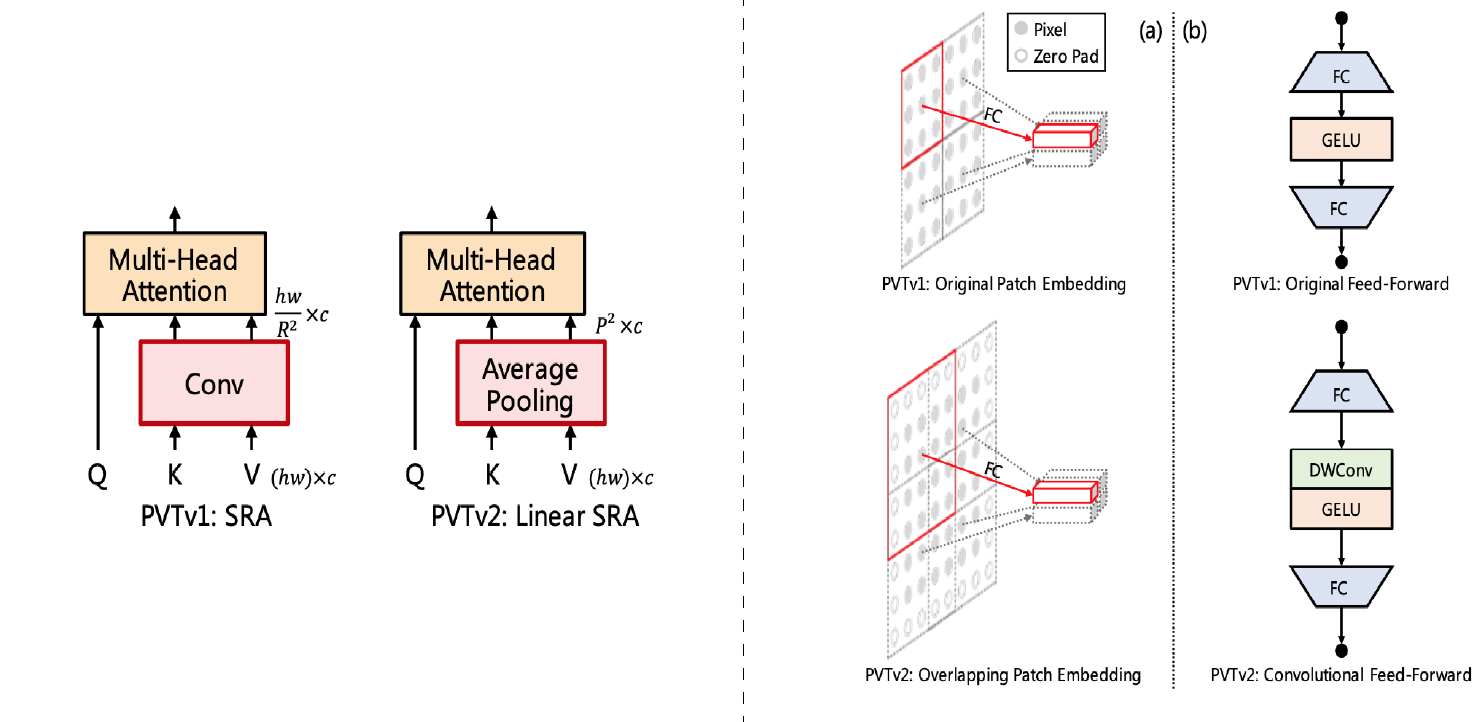
Pyramid Vision Transformer V2
Pyramid Vision Transformer V2 was introduced in here. This model is an improved version of the PVT V1. The improvements of this version are as follows:
- It uses overlapping patch embedding by using padded convolutions
- It uses convolutional feed-forward blocks which have a depth-wise convolution after the first fully-connected layer
- It uses a fixed pooling instead of convolutions for down sampling the K and V in the SRA attention mechanism (The new attention mechanism is called Linear SRA)
Usage
Defining the Model
from pvt_v2 import PVTV2 , PVTV2Stage
import tensorflow as tf
pvtV2Model = PVTV2(
num_of_classes=1000,
stages=[
PVTV2Stage(d_model=64,
windowSize=(2 , 2),
heads=1,
poolingSize=(7 , 7),
mlp_rate=2,
mlp_windowSize=(3 , 3),
layers=2,
dropout_rate=0.1),
PVTV2Stage(d_model=128,
windowSize=(2 , 2),
heads=2,
poolingSize=(7 , 7),
mlp_rate=2,
mlp_windowSize=(3 , 3),
layers=2,
dropout_rate=0.1),
PVTV2Stage(d_model=320,
windowSize=(2 , 2),
heads=5,
poolingSize=(7 , 7),
mlp_rate=2,
mlp_windowSize=(3 , 3),
layers=2,
dropout_rate=0.1),
],
dropout=0.5)
PVT Params
num_of_classes: int
number of classes used in the final prediction layerstages: list of PVTV2Stage
list of pvt v2 stagesdropout: float
dropout rate used for the prediction head
PVTStage Params
d_model: int
dimension used for theLinear SRAmechanism and the convolutional patch embeddingwindowSize: tuple(int , int)
window size used for the convolutional patch emebddingheads: int
number of heads in theLinear SRAmechanismpoolingSize: tuple(int , int)
size of the K and V after the fixed poolingmlp_rate: int
expansion rate used in the convolutional feed-forward blockmlp_windowSize: tuple(int , int)
the window size used for the depth-wise convolution in the convolutional feed-forward blocklayers: int
number of transformer encodersdropout_rate: float
dropout rate used in each transformer encoder
Inference
sampleInput = tf.random.normal(shape=(1 , 224 , 224 , 3))
output = pvtV2Model(sampleInput , training=False)
print(output.shape) # (1 , 1000)
Training
pvtV2Model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
metrics=[
tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name="accuracy"),
tf.keras.metrics.SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy(k=5 , name="top_5_accuracy"),
])
pvtV2Model.fit(
trainingData, #Tensorflow dataset of images and labels in shape of ((b , h , w , 3) , (b,))
validation_data=valData, #The same as training
epochs=100,)
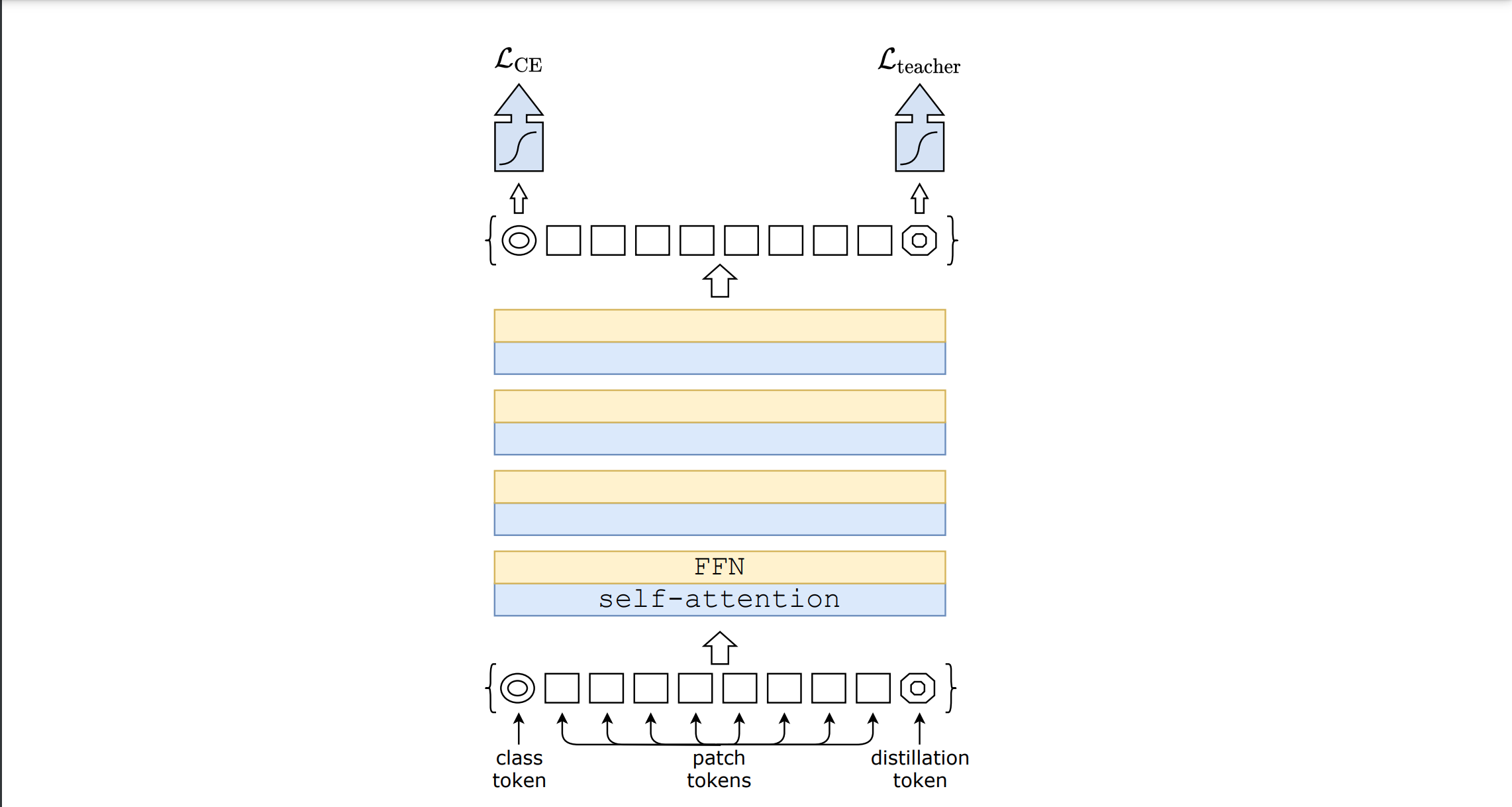
DeiT
DeiT was introduced in Training Data-Efficient Image Transformers & Distillation Through Attention. Since original vision transformer is data hungry due to the lack of existance of any inductive bias (unlike CNNs) a lot of data is required to train original vision transformer in order to surpass the state-of-the-art CNNs such as Resnet. Therefore, in this paper authors used a pre-trained CNN such as resent during training and used a sepcial loss function to perform distillation through attention.
Usage
Defining the Model
from deit import DeiT
import tensorflow as tf
teacherModel = tf.keras.applications.ResNet50(include_top=True,
weights="imagenet",
input_shape=(224 , 224 , 3))
deitModel = DeiT(
num_classes=1000,
patch_size=16,
num_of_patches=(224//16)**2,
d_model=128,
heads=2,
num_layers=4,
mlp_rate=2,
teacherModel=teacherModel,
temperature=1.0,
alpha=0.5,
hard=False,
dropout_rate=0.1,
prediction_dropout=0.3,
)
Params
num_classes: int
number of classes used for the final classification headpatch_size: int
patch_size used for the tokenizationnum_of_patches: int
number of patches after the tokenization which is used for the positional encoding, Generally it can be computed by the following formula(((h-patch_size)//patch_size) + 1)*(((w-patch_size)//patch_size) + 1)wherehis the height of the image andwis the width of the image. In addition, when height and width of the image are devisable by thepatch_sizethe following formula can be used as well(h//patch_size)*(w//patch_size)d_model: int
hidden dimension of the transformer encoder and the demnesion used for patch embeddingheads: int
number of heads used for the multi-head attention mechanismnum_layers: int
number of blocks in encoder transformermlp_rate: int
the rate of expansion in the feed-forward block of each transformer block (the dimension after expansion ismlp_rate * d_model)teacherModel: Tensorflow Model
the teacherModel used for the distillation during training, This model is a pre-trained CNN model with the same input_shape and output_shape as the Transformertemperature: float
the temperature parameter in the lossalpha: float
the coefficient balancing the Kullback–Leibler divergence loss (KL) and the cross-entropy losshard: bool
indicates using Hard-label distillation or Soft distillationdropout_rate: float
dropout rate used in the multi-head attention mechanismprediction_dropout: float
dropout rate used in the final prediction head of the model
Inference
sampleInput = tf.random.normal(shape=(1 , 224 , 224 , 3))
output = deitModel(sampleInput , training=False)
print(output.shape) # (1 , 1000)
Training
#Note that the loss is defined inside the model and no loss should be passed here
deitModel.compile(
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
metrics=[
tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name="accuracy"),
tf.keras.metrics.SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy(k=5 , name="top_5_accuracy"),
])
deitModel.fit(
trainingData, #Tensorflow dataset of images and labels in shape of ((b , h , w , 3) , (b , num_classes))
validation_data=valData, #The same as training
epochs=100,)