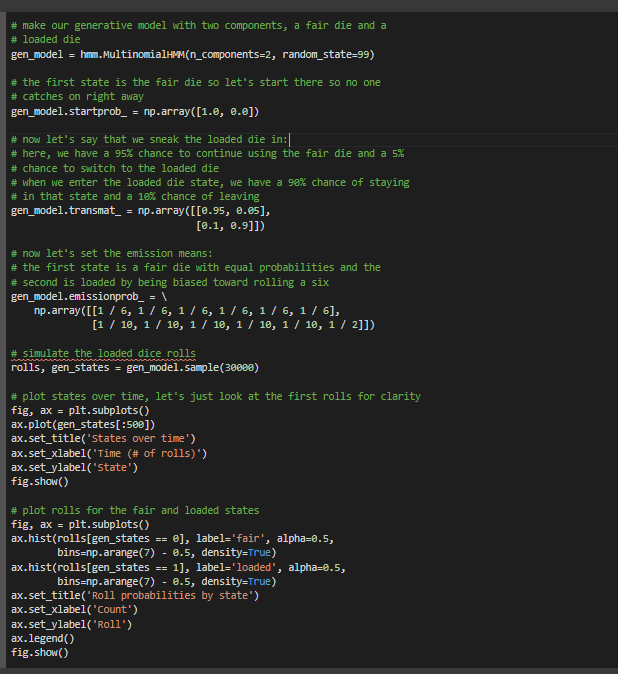
# make our generative model with two components, a fair die and a
# loaded die
gen_model = hmm.MultinomialHMM(n_components=2, random_state=99)
# the first state is the fair die so let's start there so no one
# catches on right away
gen_model.startprob_ = np.array([1.0, 0.0])
# now let's say that we sneak the loaded die in:
# here, we have a 95% chance to continue using the fair die and a 5%
# chance to switch to the loaded die
# when we enter the loaded die state, we have a 90% chance of staying
# in that state and a 10% chance of leaving
gen_model.transmat_ = np.array([[0.95, 0.05],
[0.1, 0.9]])
# now let's set the emission means:
# the first state is a fair die with equal probabilities and the
# second is loaded by being biased toward rolling a six
gen_model.emissionprob_ = \
np.array([[1 / 6, 1 / 6, 1 / 6, 1 / 6, 1 / 6, 1 / 6],
[1 / 10, 1 / 10, 1 / 10, 1 / 10, 1 / 10, 1 / 2]])
# simulate the loaded dice rolls
rolls, gen_states = gen_model.sample(30000)
# plot states over time, let's just look at the first rolls for clarity
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(gen_states[:500])
ax.set_title('States over time')
ax.set_xlabel('Time (# of rolls)')
ax.set_ylabel('State')
fig.show()
# plot rolls for the fair and loaded states
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.hist(rolls[gen_states == 0], label='fair', alpha=0.5,
bins=np.arange(7) - 0.5, density=True)
ax.hist(rolls[gen_states == 1], label='loaded', alpha=0.5,
bins=np.arange(7) - 0.5, density=True)
ax.set_title('Roll probabilities by state')
ax.set_xlabel('Count')
ax.set_ylabel('Roll')
ax.legend()
fig.show()
MultinomialHMM has undergone major changes. The previous version was implementing CategoricalHMM (a special case of MultinomialHMM). This new implementation follows the standard definition for a Multinomial distribution, e.g. as in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multinomial_distributionSee these issues for details:
https://github.com/hmmlearn/hmmlearn/issues/335
https://github.com/hmmlearn/hmmlearn/issues/340
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
[<ipython-input-9-4c6e1e68a7c1>](https://localhost:8080/#) in <module>()
22
23 # simulate the loaded dice rolls
---> 24 rolls, gen_states = gen_model.sample(30000)
25
26 # plot states over time, let's just look at the first rolls for clarity
3 frames
[/root/.local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/hmmlearn/base.py](https://localhost:8080/#) in sample(self, n_samples, random_state, currstate)
461 state_sequence = [currstate]
462 X = [self._generate_sample_from_state(
--> 463 currstate, random_state=random_state)]
464
465 for t in range(n_samples - 1):
[/root/.local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/hmmlearn/hmm.py](https://localhost:8080/#) in _generate_sample_from_state(self, state, random_state)
481 sample = multinomial.rvs(
482 n=self.n_trials, p=self.emissionprob_[state, :],
--> 483 size=1, random_state=self.random_state)
484 return sample.squeeze(0) # shape (1, nf) -> (nf,)
485
[/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/scipy/stats/_multivariate.py](https://localhost:8080/#) in rvs(self, n, p, size, random_state)
3216 %(_doc_callparams_note)s
3217 """
-> 3218 n, p, npcond = self._process_parameters(n, p)
3219 random_state = self._get_random_state(random_state)
3220 return random_state.multinomial(n, p, size)
[/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/scipy/stats/_multivariate.py](https://localhost:8080/#) in _process_parameters(self, n, p)
3016 pcond |= np.any(p > 1, axis=-1)
3017
-> 3018 n = np.array(n, dtype=np.int, copy=True)
3019
3020 # true for bad n
TypeError: int() argument must be a string, a bytes-like object or a number, not 'NoneType'



