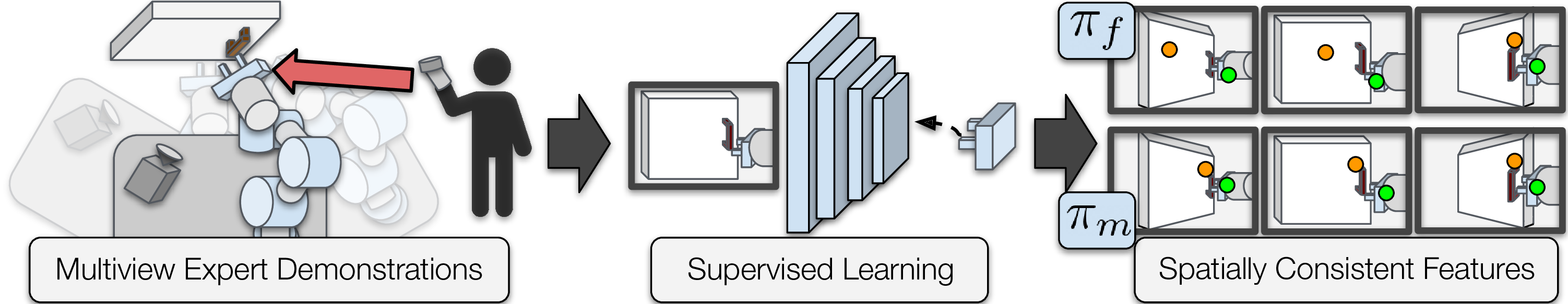
Seeing All the Angles: Learning Multiview Manipulation Policies for Contact-Rich Tasks from Demonstrations
Trevor Ablett, Daniel (Yifan) Zhai, Jonathan Kelly
Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS’21)
Paper website: https://papers.starslab.ca/multiview-manipulation/
arXiv paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.13907
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS51168.2021.9636440
This work was motivated by a relatively simple question: will increasingly popular end-to-end visuomotor policies work on a mobile manipulator, where the angle of the base will not be repeatable from one execution of a task to another? We conducted a variety of experiments to show that, naively, policies trained on fixed-base data with imitation learning do not generalize to various poses, and also generate multiview datasets and corresponding multiview policies to remedy the problem.
This repository contains the source code for reproducing our results and plots.
Requirements
We have only tested in python 3.7. Our simulated environments use pybullet, and our training code uses TensorFlow 2.x, specifically relying on our manipulator-learning package. All requirements (for simulated environments) are automatically installed by following Setup below.
Our policies also use the groups argument in TensorFlow Conv2d, which requires a GPU.
Setup
Preliminary note on TensorFlow install
This repository uses TensorFlow with GPU support, which can of course can be a bit of a pain to install. If you already have it installed, ignore this message. Otherwise, we have found the following procedure to work:
- Install conda.
- Create a new conda env to use for this work and activate it.
- Run the following to install a version of TensorFlow that may work with Conda
conda install cudatoolkit cudnn
pip install tensorflow==2.6.* tensorflow-probability==0.14
Now you can continue with the regular installation.
Regular Installation
Clone this repository and install in your python environment with pip.
git clone [email protected]:utiasSTARS/multiview-manipulation.git && cd multiview-manipulation
pip install -e .
A Note on Environment Names
The simulated environments that we use are all available in our manipulator-learning package and are called:
- ThingLiftXYZImage
- ThingLiftXYZMultiview
- ThingStackSameImageV2
- ThingStackSameMultiviewV2
- ThingPickAndInsertSucDoneImage
- ThingPickAndInsertSucDoneMultiview
- ThingDoorImage
- ThingDoorMultiview
The real environments we use with our mobile manipulator will, of course, be harder to reproduce, but were generated using our thing-gym-ros repository and are called:
- ThingRosPickAndInsertCloser6DOFImageMB
- ThingRosDrawerRanGrip6DOFImageMB
- ThingRosDoorRanGrip6DOFImage
- ThingRosDoorRanGrip6DOFImageMB
Running and Training Behavioural Cloning (BC) policies
The script in this repository can actually train and test (multiple)policies all in one shot.
-
Choose one of:
- Train and test policies all at once. Download and uncompress any of the simulated expert data (generated using an HTC Vive hand tracker) from this Google Drive Folder.
- Generate policies using the procedure outlined in the following section.
- Download policies from this Google Drive Folder. We'll assume that you downloaded
ThingDoorMultiview_bc_models.zip.
If you choose i., your folder structure should be:
. └── multiview-manipulation/ ├── multiview_manipulation/ └── data/ ├── bc_models/ └── demonstrations/ ├── ThingDoorMultiview/ ├── depth/ ├── img/ ├── data.npz └── data_swp.npzIf you choose ii. or iii., your folder structure should be:
. └── multiview-manipulation/ ├── multiview_manipulation/ └── data/ └── bc_models/ ├── ThingDoorMultiview_25_trajs_1/ ├── ThingDoorMultiview_25_trajs_2/ ├── ThingDoorMultiview_25_trajs_3/ ├── ThingDoorMultiview_25_trajs_4/ ├── ThingDoorMultiview_25_trajs_5/ ├── ThingDoorMultiview_50_trajs_1/ └── ... -
Modify the following options in
multiview_manipulation/policies/test_policies.pyto match your system and selected data:main_data_dir: top level data directory (default:data)bc_models_dir: top level trained BC models directory (default:bc_models)expert_data_dir: top level expert data directory (default:demonstrations, only required if option i. above was selected).
-
Change the following options to choose whether you want to test policies in a different environment from which they were trained in (e.g., as stated in the paper, you can test a
ThingDoorMultiviewpolicy in bothThingDoorMultiviewandThingDoorImage):env_name: environment to test policy inpolicy_env_name: name of environment that data for policy was generated from.
-
Modify the options for choosing which policies to train/test:
bc_ckpts_num_traj: The different number of trajectories to use for training/trained policies (default:range(200, 24, -25))seeds: Which seeds to use (default:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
-
Run the script:
python multiview_manipulation/policies/test_policies.py
- Your results will show up in
data/bc_results/{env_name}_{env_seed}_{experiment_name}.
Training policies with Behavioural Cloning (BC) only
-
Download and uncompress any of simulated expert data from this Google Drive Folder. We'll assume that you downloaded
ThingDoorMultiview.tar.gzand uncompressed it asThingDoorMultiview. -
Modify the following options in
multiview_manipulation/policies/gen_policies.pyto match your system and selected data:bc_models_dir: top level directory for trained BC models (default:data/bc_models)expert_data_dir: top level directory for expert data (default:data/demonstrations)dataset_dir: the name of the directory containingdepth/,img/,data.npzanddata_swp.npz.env_str: The string corresponding to the name of the environment (only used for the saved BC policy name)
For example, if you're using the default folder structure, your setup should look like this:
. └── multiview-manipulation/ ├── multiview_manipulation/ └── data/ ├── bc_models/ └── demonstrations/ ├── ThingDoorMultiview/ ├── depth/ ├── img/ ├── data.npz └── data_swp.npz -
Modify the options for choosing which policies to train:
bc_ckpts_num_traj: The different number of trajectories to use for training policies (default:range(25, 201, 25))seeds: Which seeds to train for (default:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
-
Run the file:
python multiview_manipulation/policies/gen_policies.py
- Your trained policies will show up in individual folders under the
bc_modelsfolder as{env_str}_{num_trajs}_trajs_{seed}/.
Collecting Demonstrations
All of our demonstrations were collected using the collect_demos.py file from the manipulator-learning package and an HTC Vive Hand Tracker. To collect demonstrations, you would use, for example:
git clone [email protected]:utiasSTARS/manipulator-learning.git && cd manipulator-learning
pip install -e .
pip install -r device_requirements.txt
python manipulator_learning/learning/imitation/collect_demos.py --device vr --directory demonstrations --demo_name ThingDoorMultiview01 --environment ThingDoorMultiview
You can also try using the keyboard with:
python manipulator_learning/learning/imitation/collect_demos.py --device keyboard --directory demonstrations --demo_name ThingDoorMultiview01 --environment ThingDoorMultiview
More instructions can be found in the manipulator-learning README.
Real Environments
Although it would be nearly impossible to exactly reproduce our results with our real environments, the code we used for generating our real environments can be found in our thing-gym-ros repository.
Citation
If you use this in your work, please cite:
@inproceedings{2021_Ablett_Seeing,
address = {Prague, Czech Republic},
author = {Trevor Ablett and Yifan Zhai and Jonathan Kelly},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the {IEEE/RSJ} International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems {(IROS'21)}},
date = {2021-09-27/2021-10-01},
month = {Sep. 27--Oct. 1},
site = {https://papers.starslab.ca/multiview-manipulation/},
title = {Seeing All the Angles: Learning Multiview Manipulation Policies for Contact-Rich Tasks from Demonstrations},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/2104.13907},
video1 = {https://youtu.be/oh0JMeyoswg},
year = {2021}
}