Designing a Minimal Retrieve-and-Read System for Open-Domain Question Answering
Abstract
In open-domain question answering (QA), retrieve-and-read mechanism has the inherent benefit of interpretability and the easiness of adding, removing, or editing knowledge compared to the parametric approaches of closed-book QA models. However, it is also known to suffer from its large storage footprint due to its document corpus and index. Here, we discuss several orthogonal strategies to drastically reduce the footprint of a retrieve-and-read open-domain QA system by up to 160x. Our results indicate that retrieve-and-read can be a viable option even in a highly constrained serving environment such as edge devices, as we show that it can achieve better accuracy than a purely parametric model with comparable docker-level system size.
- Paper (To appear in NAACL 2021)
- Authors: Sohee Yang and Minjoon Seo
- Live Web Demo
- BibTeX:
@inproceedings{mininalrnr,
title={Designing a Minimal Retrieve-and-Read System for Open-Domain Question Answering},
author={Yang, Sohee and Seo, Minjoon},
booktitle={NAACL},
year={2021}
}
This repository contains the code of the Minimal Retrieve & Read QA System that ranked the first place in the human (manual) evaluation and the second place in the automatic evaluation on "Systems Under 500Mb Track" of the NeurIPS 2020 EfficientQA competition.
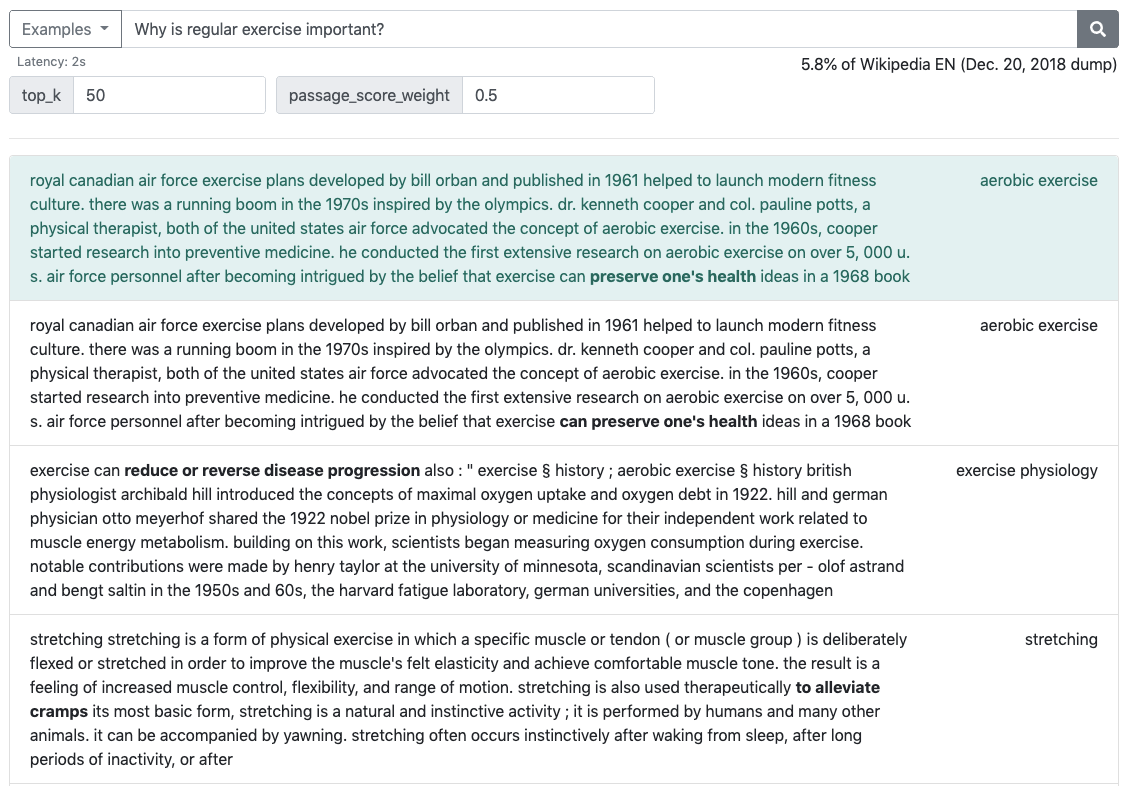
Web Demo
You can play with the QA system in the Live Web Demo. You can also dynamically change the inference setting by controlling the values of top_k and passage_score_weight.
top_k: sets the number of passages to retrieve and pass to the reader. The value must be a positive integer. Default value is set to 50. For the live web demo, the values are limited within the range [1, 100] to prevent freezing from reading too many passages.passage_score_weight:- When the default value
nullis used, only the passage with the highest ranking score is used to extract the answers from. This is the setting used in DPR. - If a float value (λ ∈ [0, 1] highly recommended) is given, multiple passages are considered to select the answer. Specifically, answer spans from multiple passages are scored using the weighted sum of passage ranking scores and answer spans scores. The weighted sum is calculated as (1 - λ) (log Pstart + log Pend) + 2λ log Prank. Please refer to the paper for more details.
- When the default value
If you have Docker installed, you can also run the web demo on your local machine in five minutes using this command.
A. Introduction
This repository contains the code for an interactive web demo, code for inference on the questions in a file (and evaluation on the answers), links to the model graphs/checkpoints (models), links to the index and preprocessed corpus files (resources), and links to built docker images.
competitiondirectory contains the code to build and run the minimal-sized docker container used for the EfficientQA competition. Typingdu -h /in the launched container reports 484.68MB as its size. Please see E. Competition Setting: Build & Run for detail.playgrounddirectory contains more practical, refactored code to play with that one can either run a web demo or run inference on a file using models built in different settings. Please see D. Playground: Build & Run for detail.
B. Local Web Demo Quickstart
To run the web demo on your local machine, run the following using docker:
docker run \
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro \
--oom-kill-disable=true \
--env MODE=demo \
-p 10001:10001 \
soheeyang/minimal-rnr-qa:effqa-tfserving \
/workspace/entrypoint.sh
Then, access http://localhost:10001 to play with the demo!
C. Pre-Built Docker Images
Available in https://hub.docker.com/r/soheeyang/minimal-rnr-qa
- soheeyang/minimal-rnr-qa:$DATASET-$MODEL_TYPE
- $DATASET: [ effqa | nq | trivia ]
- $MODEL_TYPE: [ tfserving | tfserving_faiss | pytorch ]
- soheeyang/minimal-rnr-qa:$DATASET-competition
- $DATASET: [ effqa | nq | trivia ]
soheeyang/minimal-rnr-qa:effqa-competitionis the docker container used for the EfficientQA challenge
The follwoing are descriptions for each of the options for DATASET and MODEL_TYPE.
$DATASETis used to select the model; The model trained on this dataset is selected. The value must be one of the followings.effqatrained on Natural Questions (NQ) train set, validation done on EfficientQA dev setnqtrained on NQ train set, validation done on NQ dev settriviatrained on TriviaQA (Trivia) train set, validation done on Trivia dev set
$MODEL_TYPEis used to select the type of the chosen model. The value must be one of the followings.tfservingTensorFlow (TF) graph for TF Serving. Index is fused into the graph to perform efficient passage retrieval without additional library dependency. This is the setting used in the EfficientQA competition. CPU serving. Smallest system footprint.tfserving_faissTF graph for TF Serving, but without index. It installs and makes use of FAISS to perform passage retrieval. CPU serving.pytorchPyTorch checkpoint. It installs and makes use of FAISS to perform passage retrieval. The model code can be found atplayground/workspace/minimal_rnr/pytorch/model.py. Supports serving on both CPU & GPU. Largest system footprint.
D. Playground: Build & Run
You can skip steps 1 and 2 if you use the pre-built docker images.
1. Download the code and necessary resources
git clone https://github.com/clovaai/minimal-rnr-qa.git
cd minimal-rnr-qa/playground
wget https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/l7034dttyp4bbf2/minrnr_playground_models.tar.gz
wget https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/51g36ytprbcl3mv/minrnr_playground_resources.tar.gz
tar xvf minrnr_playground_models.tar.gz
tar xvf minrnr_playground_resources.tar.gz
2. Build docker image
# inside minimal-rnr-qa/playground
DATASET=effqa
MODEL_TYPE=tfserving
chmod a+x ./build.sh
./build.sh $DATASET $MODEL_TYPE
- This command builds a docker image tagged as
minimal-rnr-qa:$DATASET-$MODEL_TYPE.
3-1. Run web demo
docker run \
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro \
--oom-kill-disable=true \
--env MODE=demo \
-p 10001:10001 \
minimal-rnr-qa:$DATASET-$MODEL_TYPE \
/workspace/entrypoint.sh
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:rosets the timezone of the container to be same with the host's.--oom-kill-disable=trueprevents kill by OOM.--env MODE=demo[REQUIRED] runs a web demo.-p $HOST_PORT:10001[REQUIRED] sets the port of the web page. connects the port 10001 of the container to a port of the host.minimal-rnr-qa:$DATASET-$MODEL_TYPE[REQUIRED] Tag of the built image./workspace/entrypoint.sh[REQUIRED] Entrypoint of the container.
3-2. Run inference on a file
Download input data
The input files for EfficientQA dev set, NQ dev & test set, and Trivia dev & test set can be downloaded at once.
INPUT_DIR=/tmp/minimal-rnr-qa
OUTPUT_DIR=/tmp/minimal-rnr-qa
mkdir -p $INPUT_DIR
mkdir -p $OUTPUT_DIR
wget -P $INPUT_DIR https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/juh12j1z0ct3zeu/minrnr_datasets.tar.gz
tar xvf $INPUT_DIR/minrnr_datasets.tar.gz -C $INPUT_DIR --strip-components=1
Run inference
INPUT_FILE_NAME=NQ-open.efficientqa.dev.1.1.jsonl
OUTPUT_FILE_NAME=NQ-open.efficientqa.dev.1.1-predictions.jsonl
TOP_K=80
PASSAGE_W=0.8
docker run \
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro \
--oom-kill-disable=true \
-v $INPUT_DIR:/input \
-v $OUTPUT_DIR:/output \
--env MODE=file \
--env TOP_K=$TOP_K \
--env PASSAGE_W=$PASSAGE_W \
minimal-rnr-qa:$DATASET-$MODEL_TYPE \
/workspace/entrypoint.sh \
/input/$INPUT_FILE_NAME \
/output/$OUTPUT_FILE_NAME
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:rosets the timezone of the container to be same with the host's.--oom-kill-disable=trueprevents kill by OOM.-v $INPUT_DIR:/input[REQUIRED] maps$INPUT_DIRof the host to/inputin the container where the data is read from. This directory must have the file to run inference on.-v $OUTPUT_DIR:/output[OPTIONAL] maps$OUTPUT_DIRof the host to/outputin the container where the prediction result file is written. If not specified, the output prediction file is written only in the container.--env MODE=demo[REQUIRED] runs inference on the given input file and outputs the predictions--env TOP_K=$INT_VALUE[OPTIONAL] sets the number of passages to retrieve and pass to the reader. It must be an integer value. Default value is set to 50.--env PASSAGE_W=$FLOAT_VALUE[OPTIONAL]- If the option is not used (as default) or
nullis given as the value, only the passage with the highest ranking score is used to extract the answers from. This is the setting used in DPR. - If the value is given, multiple passages are considered to select the answer. Specifically, answer spans from multiple passages are scored using the weighted sum of passage ranking scores and answer spans scores. The given value for this option must be λ ∈ [0, 1], and the weighted sum is calculated as (1 - λ) (log Pstart + log Pend) + 2λ log Prank. This value may be tuned on the validation set to slightly raise the end-to-end question answering accuracy.
- If the option is not used (as default) or
minimal-rnr-qa:$DATASET_$MODEL_TYPE[REQUIRED] Tag of the built image./workspace/entrypoint.sh[REQUIRED] Entrypoint of the container./input/$INPUT_FILE_NAME[REQUIRED] Name of the file to run inference on. CSV or JSON Lines files are supported.- CSV files must consist of row of question strings or
question\t["answer_1", ..., "answer_n"]. - JSON Lines files must consist of rows of
{"question": ...},{"question": ..., "answers": ...}, or{"question": ..., "answer": ...}. - If answers exist, Exact Match (EM) score is calculated and reported at the end of the inference.
- CSV files must consist of row of question strings or
/output/$OUTPUT_FILE_NAME[REQUIRED] Name of the output prediction result file. The file takes JSON Lines format. Please note that even if "answer" is given as the key for answers in the input file, it changes to "answers" in the prediction file for consistency and easier evaluation.
E. Competition Setting: Build & Run
You can skip steps 1 and 2 if you use the pre-built docker images.
1. Download the code and necessary resources
git clone https://github.com/clovaai/minimal-rnr-qa.git
cd minimal-rnr-qa/competition
wget https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/s5fa4rgf48bhhkb/minrnr_competition_resources.tar.gz
wget https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/utwzozvuret1sdo/minrnr_competition_models.tar.gz
tar xvf minrnr_competition_models.tar.gz
tar xvf minrnr_competition_resources.tar.gz
2. Build docker image
# inside minimal-rnr-qa/competition
DATASET=effqa
chmod a+x ./build.sh
./build.sh $DATASET
- Values for
$DATASETeffqa: the model used in the challenge (Section 3 in the paper)nq: trained on Natural Questions (Appendix A.5 in the paper)trivia: trained on TriviaQA (Appendix A.5 in the paper)
- This command builds a docker image tagged as
minimal-rnr-qa:$DATASET-competition.
3. Prepare data (same as the above)
The input files for EfficientQA dev set, NQ dev & test set, and Trivia dev & test set can be downloaded at once.
INPUT_DIR=/tmp/minimal-rnr-qa
OUTPUT_DIR=/tmp/minimal-rnr-qa
mkdir -p $INPUT_DIR
mkdir -p $OUTPUT_DIR
wget -P $INPUT_DIR https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/juh12j1z0ct3zeu/minrnr_datasets.tar.gz
tar xvf $INPUT_DIR/minrnr_datasets.tar.gz -C $INPUT_DIR --strip-components=1
4. Run
# The setting used for EfficientQA submission
INPUT_FILE_NAME=NQ-open.efficientqa.dev.1.1.jsonl
OUTPUT_FILE_NAME=NQ-open.efficientqa.dev.1.1-predictions.jsonl
TOP_K=80
PASSAGE_W=0.8
docker run \
-v ${INPUT_DIR}:/input \
-v ${OUTPUT_DIR}:/output \
--env TOP_K=$TOP_K \
--env PASSAGE_W=$PASSAGE_W \
--network="none" \
--oom-kill-disable=true \
minimal-rnr-qa:$DATASET-competition \
/submission.sh \
/input/$INPUT_FILE_NAME \
/output/$OUTPUT_FILE_NAME
- Below are the parameters to reproduce each of the results of the last row in Table 3 (in the Appendix of the paper).
- EfficientQA dev
- DATASET=effqa / TOP_K=80 / PASSAGE_W=null
- INPUT_FILE_NAME=NQ-open.efficientqa.dev.1.1.jsonl (from this link)
- While 34.33 is reported in the paper, the value changed to 34.55 after we rebuilt the TensorFlow graph w.r.t. refactoring. The model supported here is the latter one.
- NQ dev
- DATASET=nq / TOP_K=100 / PASSAGE_W=null
- INPUT_FILE_NAME=nq-dev.jsonl
- NQ test
- DATASET=nq / TOP_K=90 / PASSAGE_W=null
- INPUT_FILE_NAME=nq-test.jsonl
- Trivia dev
- DATASET=trivia / TOP_K=100 / PASSAGE_W=null
- INPUT_FILE_NAME=trivia-dev.jsonl
- Trivia test
- DATASET=trivia / TOP_K=100 / PASSAGE_W=null
- INPUT_FILE_NAME=trivia-test.jsonl
- EfficientQA dev
F. License
Copyright 2021-present NAVER Corp.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.