Steps to run =>
- Download the cora dataset from this link : https://linqs.soe.ucsc.edu/data
- unzip the files in the folder input/cora
- cd code
- python eda.py
- python word_features_only.py # for baseline model 53.28% accuracy
- python graph_embedding.py # for model_1 73.06% accuracy
- python graph_features_embedding.py # for model_2 76.35% accuracy
Learning from Graph data using Keras and Tensorflow
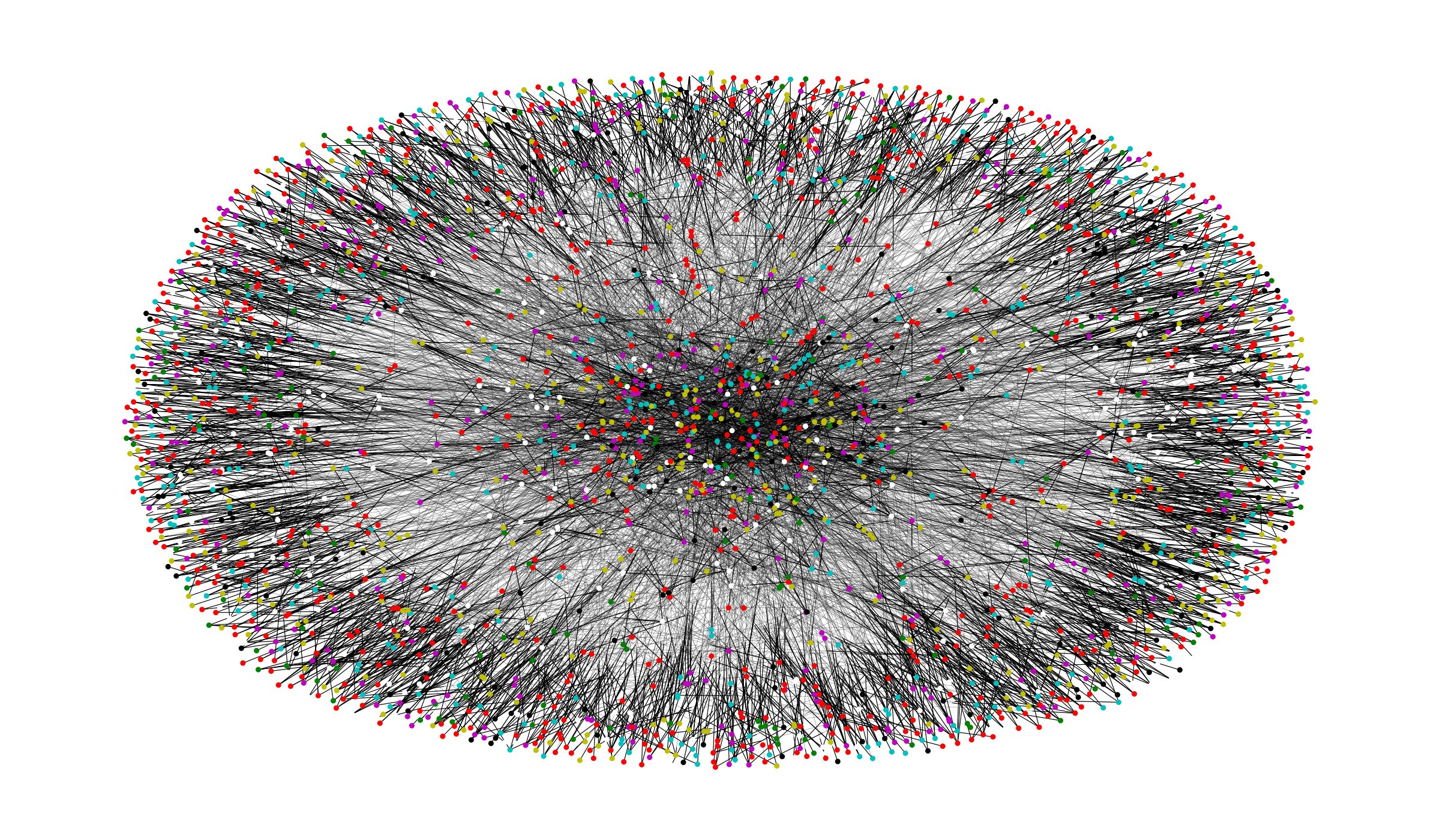
Cora Data set Citation Graph
Motivation :
There is a lot of data out there that can be represented in the form of a graph in real-world applications like in Citation Networks, Social Networks (Followers graph, Friends network, … ), Biological Networks or Telecommunications.
Using Graph extracted features can boost the performance of predictive models by relying of information flow between close nodes. However, representing graph data is not straightforward especially if we don’t intend to implement hand-crafted features.
In this post we will explore some ways to deal with generic graphs to do node classification based on graph representations learned directly from data.
Dataset :
The Cora citation network data set will serve as the base to the implementations and experiments throughout this post. Each node represents a scientific paper and edges between nodes represent a citation relation between the two papers.
Each node is represented by a set of binary features ( Bag of words ) as well as by a set of edges that link it to other nodes.
The dataset has 2708 nodes classified into one of seven classes. The network has 5429 links. Each Node is also represented by a binary word features indicating the presence of the corresponding word. Overall there is 1433 binary (Sparse) features for each node. In what follows we only use 140 samples for training and the rest for validation/test.
Problem Setting :
Problem : Assigning a class label to nodes in a graph while having few training samples.
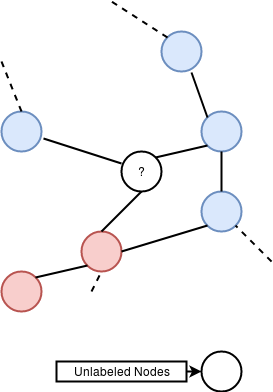
Intuition/Hypothesis : Nodes that are close in the graph are more likely to have similar labels.
Solution : Find a way to extract features from the graph to help classify new nodes.
Proposed Approach :
Baseline Model :
Simple Baseline Model
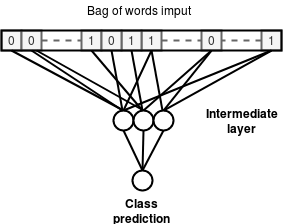
We first experiment with the simplest model that learn to predict node classes using only the binary features and discarding all graph information.
This model is a fully-connected Neural Network that takes as input the binary features and outputs the class probabilities for each node.
Baseline model Accuracy : 53.28%
****This is the initial accuracy that we will try to improve on by adding graph based features.
Adding Graph features :
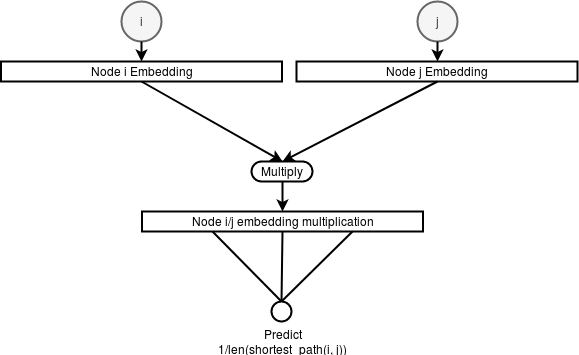
One way to automatically learn graph features by embedding each node into a vector by training a network on the auxiliary task of predicting the inverse of the shortest path length between two input nodes like detailed on the figure and code snippet below :
Learning an embedding vector for each node
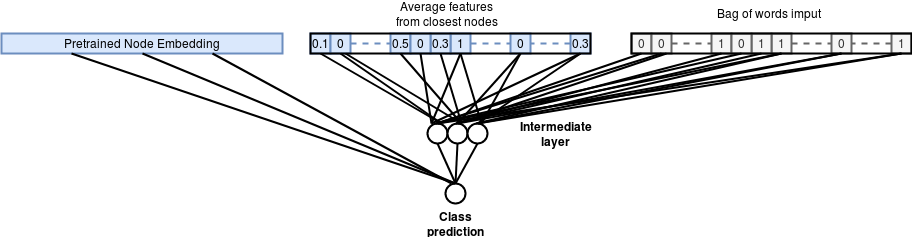
The next step is to use the pre-trained node embedding as input to the classification model. We also add the an additional input which is the average binary features of the neighboring nodes using distance of learned embedding vectors.
The resulting classification network is described in the following figure :
Using pretrained embeddings to do node classification
Graph embedding classification model Accuracy : 73.06%
We can see that adding learned graph features as input to the classification model helps significantly improve the classification accuracy compared to the baseline model from **53.28% to 73.06% **
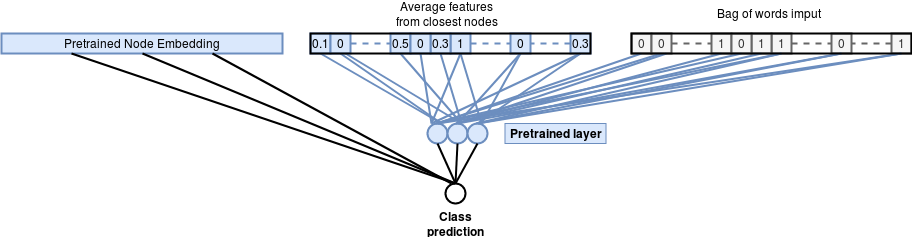
Improving Graph feature learning :
We can look to further improve the previous model by pushing the pre-training further and using the binary features in the node embedding network and reusing the pre-trained weights from the binary features in addition to the node embedding vector. This results in a model that relies on more useful representations of the binary features learned from the graph structure.
Improved Graph embedding classification model Accuracy : 76.35%
This additional improvement adds a few percent accuracy compared to the previous approach.
Conclusion :
In this post we saw that we can learn useful representations from graph structured data and then use these representations to improve the generalization performance of a node classification model from **53.28% to 76.35% **
Code to reproduce the results is available here : https://github.com/CVxTz/graph_classification