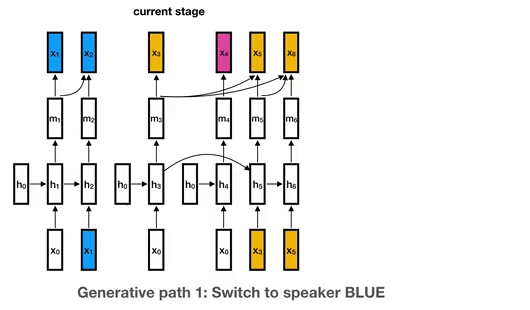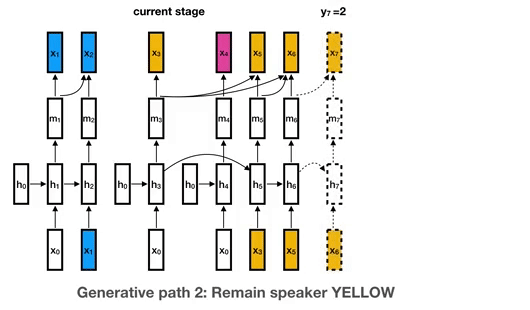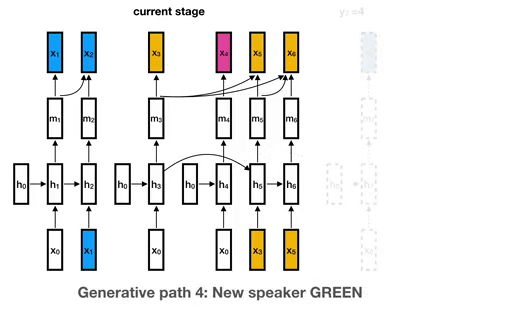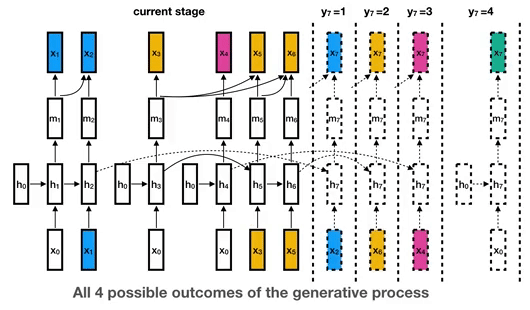
UIS-RNN
Overview
This is the library for the Unbounded Interleaved-State Recurrent Neural Network (UIS-RNN) algorithm. UIS-RNN solves the problem of segmenting and clustering sequential data by learning from examples.
This algorithm was originally proposed in the paper Fully Supervised Speaker Diarization.
The work has been introduced by Google AI Blog.
Disclaimer
This open source implementation is slightly different than the internal one which we used to produce the results in the paper, due to dependencies on some internal libraries.
We CANNOT share the data, code, or model for the speaker recognition system (d-vector embeddings) used in the paper, since the speaker recognition system heavily depends on Google's internal infrastructure and proprietary data.
This library is NOT an official Google product.
We welcome community contributions (guidelines) to the uisrnn/contrib folder. But we won't be responsible for the correctness of any community contributions.
Dependencies
This library depends on:
- python 3.5+
- numpy 1.15.1
- pytorch 1.3.0
- scipy 1.1.0 (for evaluation only)
Getting Started
Install the package
Without downloading the repository, you can install the package by:
pip3 install uisrnn
or
python3 -m pip install uisrnn
Run the demo
To get started, simply run this command:
python3 demo.py --train_iteration=1000 -l=0.001
This will train a UIS-RNN model using data/toy_training_data.npz, then store the model on disk, perform inference on data/toy_testing_data.npz, print the inference results, and save the averaged accuracy in a text file.
PS. The files under data/ are manually generated toy data, for demonstration purpose only. These data are very simple, so we are supposed to get 100% accuracy on the testing data.
Run the tests
You can also verify the correctness of this library by running:
bash run_tests.sh
If you fork this library and make local changes, be sure to use these tests as a sanity check.
Besides, these tests are also great examples for learning the APIs, especially tests/integration_test.py.
Core APIs
Glossary
| General Machine Learning | Speaker Diarization |
|---|---|
| Sequence | Utterance |
| Observation / Feature | Embedding / d-vector |
| Label / Cluster ID | Speaker |
Arguments
In your main script, call this function to get the arguments:
model_args, training_args, inference_args = uisrnn.parse_arguments()
Model construction
All algorithms are implemented as the UISRNN class. First, construct a UISRNN object by:
model = uisrnn.UISRNN(args)
The definitions of the args are described in uisrnn/arguments.py. See model_parser.
Training
Next, train the model by calling the fit() function:
model.fit(train_sequences, train_cluster_ids, args)
The definitions of the args are described in uisrnn/arguments.py. See training_parser.
The fit() function accepts two types of input, as described below.
Input as list of sequences (recommended)
Here, train_sequences is a list of observation sequences. Each observation sequence is a 2-dim numpy array of type float.
- The first dimension is the length of this sequence. And the length can vary from one sequence to another.
- The second dimension is the size of each observation. This must be consistent among all sequences. For speaker diarization, the observation could be the d-vector embeddings.
train_cluster_ids is also a list, which has the same length as train_sequences. Each element of train_cluster_ids is a 1-dim list or numpy array of strings, containing the ground truth labels for the corresponding sequence in train_sequences. For speaker diarization, these labels are the speaker identifiers for each observation.
When calling fit() in this way, please be very careful with the argument --enforce_cluster_id_uniqueness.
For example, assume:
train_cluster_ids = [['a', 'b'], ['a', 'c']]
If the label 'a' from the two sequences refers to the same cluster across the entire dataset, then we should have enforce_cluster_id_uniqueness=False; otherwise, if 'a' is only a local indicator to distinguish from 'b' in the 1st sequence, and to distinguish from 'c' in the 2nd sequence, then we should have enforce_cluster_id_uniqueness=True.
Also, please note that, when calling fit() in this way, we are going to concatenate all sequences and all cluster IDs, and delegate to the next section below.
Input as single concatenated sequence
Here, train_sequences should be a single 2-dim numpy array of type float, for the concatenated observation sequences.
For example, if you have M training utterances, and each utterance is a sequence of L embeddings. Each embedding is a vector of D numbers. Then the shape of train_sequences is N * D, where N = M * L.
train_cluster_ids is a 1-dim list or numpy array of strings, of length N. It is the concatenated ground truth labels of all training data.
Since we are concatenating observation sequences, it is important to note that, ground truth labels in train_cluster_id across different sequences are supposed to be globally unique.
For example, if the set of labels in the first sequence is {'A', 'B', 'C'}, and the set of labels in the second sequence is {'B', 'C', 'D'}. Then before concatenation, we should rename them to something like {'1_A', '1_B', '1_C'} and {'2_B', '2_C', '2_D'}, unless 'B' and 'C' in the two sequences are meaningfully identical (in speaker diarization, this means they are the same speakers across utterances). This part will be automatically taken care of by the argument --enforce_cluster_id_uniqueness for the previous section.
The reason we concatenate all training sequences is that, we will be resampling and block-wise shuffling the training data as a data augmentation process, such that we result in a robust model even when there is insufficient number of training sequences.
Training on large datasets
For large datasets, the data usually could not be loaded into memory at once. In such cases, the fit() function needs to be called multiple times.
Here we provide a few guidelines as our suggestions:
- Do not feed different datasets into different calls of
fit(). Instead, for each call offit(), the input should cover sequences from different datasets. - For each call to the
fit()function, make the size of input roughly the same. And, don't make the input size too small.
Prediction
Once we are done with training, we can run the trained model to perform inference on new sequences by calling the predict() function:
predicted_cluster_ids = model.predict(test_sequences, args)
Here test_sequences should be a list of 2-dim numpy arrays of type float, corresponding to the observation sequences for testing.
The returned predicted_cluster_ids is a list of the same size as test_sequences. Each element of predicted_cluster_ids is a list of integers, with the same length as the corresponding test sequence.
You can also use a single test sequence for test_sequences. Then the returned predicted_cluster_ids will also be a single list of integers.
The definitions of the args are described in uisrnn/arguments.py. See inference_parser.
Citations
Our paper is cited as:
@inproceedings{zhang2019fully,
title={Fully supervised speaker diarization},
author={Zhang, Aonan and Wang, Quan and Zhu, Zhenyao and Paisley, John and Wang, Chong},
booktitle={International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)},
pages={6301--6305},
year={2019},
organization={IEEE}
}
References
Baseline diarization system
To learn more about our baseline diarization system based on unsupervised clustering algorithms, check out this site.
A Python re-implementation of the spectral clustering algorithm used in this paper is available here.
The ground truth labels for the NIST SRE 2000 dataset (Disk6 and Disk8) can be found here.
For more public resources on speaker diarization, check out awesome-diarization.
Speaker recognizer/encoder
To learn more about our speaker embedding system, check out this site.
We are aware of several third-party implementations of this work:
- Resemblyzer: PyTorch implementation by resemble-ai
- TensorFlow implementation by Janghyun1230
- PyTorch implementaion by HarryVolek - with UIS-RNN integration
- PyTorch implementation as part of SV2TTS
Please use your own judgement to decide whether you want to use these implementations.
We are NOT responsible for the correctness of any third-party implementations.
Variants
Here we list the repositories that are based on UIS-RNN, but integrated with other technologies or added some improvements.
| Link | Description |
|---|---|
taylorlu/Speaker-Diarization  |
Speaker diarization using UIS-RNN and GhostVLAD. An easier way to support openset speakers. |
DonkeyShot21/uis-rnn-sml  |
A variant of UIS-RNN, for the paper Supervised Online Diarization with Sample Mean Loss for Multi-Domain Data. |