LWCC: A LightWeight Crowd Counting library for Python
LWCC is a lightweight crowd counting framework for Python. It wraps four state-of-the-art models all based on convolutional neural networks: CSRNet, Bayesian crowd counting, DM-Count, and SFANet. The library is based on PyTorch.
Installation
The easiest way to install library LWCC and its prerequisites is to use the package manager pip.
pip install lwcc
Usage
You can import the library and use its functionalities by:
from lwcc import LWCC
Count estimation
Most straightforward way to use the library:
img = "path/to/image"
count = LWCC.get_count(img)
This uses CSRNet pretrained on SHA (default). You can choose a different model pretrained on different data set using:
count = LWCC.get_count(img, model_name = "DM-Count", model_weights = "SHB")
The result is a float with predicted count.
Large images
Note: By default all images are resized such that the longest side is less than 1000px, preserving the aspect ratio. Otherwise models might perform worse for large images with sparse crowds (counting patterns on shirts, dresses). If you are estimating dense crowds, we recommend you to set the resize_img to False. The call should look like this:
count = LWCC.get_count(img, model_name = "DM-Count", model_weights = "SHB", resize_img = True)
Multiple images
Library allows prediction of count for multiple images with a single call of get_count. You can simply pass a list of image paths:
img1 = "path/to/image1"
img2 = "path/to/image2"
count = LWCC.get_count([img1, img2])
Result is then a dictionary of pairs image_name : image_count: 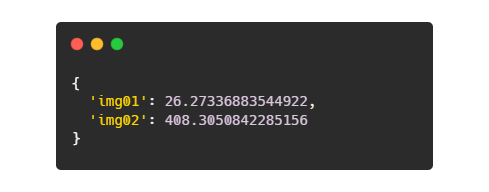
Density map
You can also request a density map by setting flag return_density = True. The result is then a tuple (count, density_map), where density_map is a 2d array with predicted densities. The array is smaller than the input image and its size depends on the model.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
count, density = LWCC.get_count(img, return_density = True)
plt.imshow(density)
plt.show()
This also works for multiple images (list of image paths as input). Result is then a tuple of two dictionaries, where the first dictionary is the same as above (pairs of image_name : image_count) and the second dictionary contains pairs of image_name : density_map.
Loading the model
You can also directly access the PyTorch models by loading them first with the load_model method.
model = LWCC.load_model(model_name = "DM-Count", model_weights = "SHA")
The loaded model is a PyTorch model and you can access its weights as with any other PyTorch model.
You can use it for inference as:
count = LWCC.get_count(img, model = model)
Models
LWCC currently offers 4 models (CSRNet, Bayesian crowd counting, DM-Count, SFANet) pretrained on Shanghai A, Shanghai B, and UCF-QNRF datasets. The following table shows the model name and MAE / MSE result of the available pretrained models on the test sets.
| Model name | SHA | SHB | QNRF |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSRNet | 75.44 / 113.55 | 11.27 / 19.32 | Not available |
| Bay | 66.92 / 112.07 | 8.27 / 13.56 | 90.43 / 161.41 |
| DM-Count | 61.39 / 98.56 | 7.68 / 12.66 | 88.97 / 154.11 |
| SFANet | Not available | 7.05 / 12.18 | Not available |
Valid options for model_name are written in the first column and thus include: CSRNet, Bay, DM-Count, and SFANet. Valid options for model_weights are written in the first row and thus include: SHA, SHB, and QNRF.
Note: Not all model_weights are supported with all model_names. See the above table for possible combinations.
How does it work?
The goal of crowd counting methods is to determine the number of people present in a particular area. There exist many approaches (detection, regression, density-based approaches), however, since 2015 many convolutional neural network (CNN) based approaches have been proposed. The basic idea behind CNN based approaches is that they normally try to predict the density map from the input image and infer the count from it. These models differ in the use of different backbones, loss functions, additional maps, etc. If you are interested in a particular algorithm, you are welcome to read the paper belonging to the specific model.
FAQ - Frequently asked questions
Can I see some more examples of LWCC in action?
Yes, you can find some examples in Examples.ipynb!
How accurate are the models?
You can see the mean absolute error (MAE) and mean squared error (MSE) of the pretrained models on test sets in section models. We recommend models pretrained on SHA or QNRF for dense crowds, and SHB for sparse crowds.
Is GPU support available?
No, GPU support is currently not supported yet, but is planned for the future version.
Can I load custom weights?
Full support of loading custom pretrained weights is not supported, but is planned in the future version.
Can I train the models myself?
The library does not support training, only inference.
Why are my results bad?
This might depend on the model you use, image size, density or type of the crowd, or the weights that you use. For example, models might often make mistakes for images with a group portrait, as they are trained on images containing crowds on streets, concerts, etc. Using SHAweights on relatively sparse crowds might also give very wrong results. On the other hand, SHB might perform better as the weights were trained on Shanghai B data set, which containts images with relatively sparse crowds. Using high quality images with sparse crowds might also yield bad results, as the algorithms might mistake some textures of clothings for a crowd.
As a rule of thumb, you should use SHB if you are planning on estimating the number of people in images with sparse crowds, and SHA or QNRF for images with dense crowds. Keep in mind that current algorithms predict the density, and there still might be some mistakes. You are welcome to try out different combinations of models and weights and see which one works the best for your problem.
Support
If you like the library please show us your support by
If you wish to include your own crowd counting model, please contact us ([email protected] or [email protected]).
Stargazers
Citation
This library is a result of a research of CNN Crowd Counting models by Matija Teršek and Maša Kljun. Although the paper has not been published yet, please provide the link to this GitHub repository if you use LWCC in your research.
License
This library is licensed under MIT license (see LICENSE). Licenses of the models wrapped in the library will be inherited, depending on the model you use ( CSRNet, Bayesian crowd counting, DM-Count, and SFANet).