Learning a Probabilistic Latent Space of Object Shapes via 3D Generative-Adversarial Modeling
This repository contains pre-trained models and sampling code for the 3D Generative Adversarial Network (3D-GAN) presented at NIPS 2016.
Prerequisites
Torch
We use Torch 7 (http://torch.ch) for our implementation with these additional packages:
matioorfb.mattorch: we use.matfile for saving voxelized shapes.
Visualization
- Basic visualization: MATLAB (tested on R2016b)
- Advanced visualization: Python 2.7 with package
numpy,matplotlib,scipyandvtk(version 5.10.1)
Note: for advanced visualization, the version of vtk has to be 5.10.1, not above. It is available in the package list of common Python distributions like Anaconda
Installation
Our current release has been tested on Ubuntu 14.04.
Cloning the repository
git clone [email protected]:zck119/3dgan-release.git
cd 3dgan-release
Downloading pretrained models
For CPU (947 MB):
./download_models_cpu.sh
For GPU (618 MB):
./download_models_gpu.sh
Downloading latent vector inputs for demo
./download_demo_inputs.sh
Guide
Synthesizing shapes (main.lua)
We show how to synthesize shapes with our pre-trained models. The file (main.lua) has the following options.
-gpu ID: GPUID(starting from 1). Set to 0 to use CPU only.-class CLASSNAME: synthesize shapes for the classCLASSNAME. We currently support five classes (car,chair,desk,gun, andsofa). Useallto generate shapes for each class.-sample: whether to sample input latent vectors from an i.i.d. uniform distribution, or to generate shapes with demo vectors loaded from./demo_inputs/CLASSNAME.mat-bs BATCH_SIZE: use batch size ofBATCH_SIZEduring network forwarding-ss SAMPLE_SIZE: set the number of generated shapes toSAMPLE_SIZE. This option is only available in-samplemode.
Usages include
- Synthesize chairs with pre-sampled demo inputs and a CPU
th main.lua -gpu 0 -class chair
- Randomly sample 150 desks with GPU 1 and a batch size of 50
th main.lua -gpu 1 -class desk -bs 50 -sample -ss 150
- Randomly sample 150 shapes of each category with GPU 1 and a batch size of 50
th main.lua -gpu 1 -class all -bs 50 -sample -ss 150
The output is saved under folder ./output, with class_name_demo.mat for shapes generated by predetermined demo inputs (z in our paper), and class_name_sample.mat for randomly sampled 3D shapes. The variable inputs in the .mat file correponds to the input latent representation, and the variable voxels corresponds to the generated 3D shapes by our network.
Visualization
We offer two ways of visualizing results, one in MATLAB and the other in Python. We used the Python visualization in our paper. The MATLAB visualization is easier to install and run, but its output has a lower quality compared with the Python one.
MATLAB: Please use the function visualization/matlab/visualize.m for visualization. The MATLAB code allows users to either display rendered objects or save them as images. The script also supports downsampling and thresholding for faster rendering. The color of voxels represents the confidence value.
Options include
inputfile: the .mat file that saves the voxel matricesindices: the indices of objects in the inputfile that should be rendered. The default value is 0, which stands for rendering all objects.step (s): downsample objects via a max pooling of step s for efficiency. The default value is 4 (64 x 64 x 64 -> 16 x 16 x 16).threshold: voxels with confidence lower than the threshold are not displayedoutputprefix:- when not specified, Matlab shows figures directly.
- when specified, Matlab stores rendered images of objects at
outputprefix_%i.bmp, where%iis the index of objects
Usage (after running th main.lua -gpu 0 -class chair, in MATLAB, in folder visualization/matlab):
visualize('../../output/chair_demo.mat', 0, 2, 0.1, 'chair')
The visualization might take a while. The obtained rendering (chair_1/3/4/5.bmp) should look as follows.
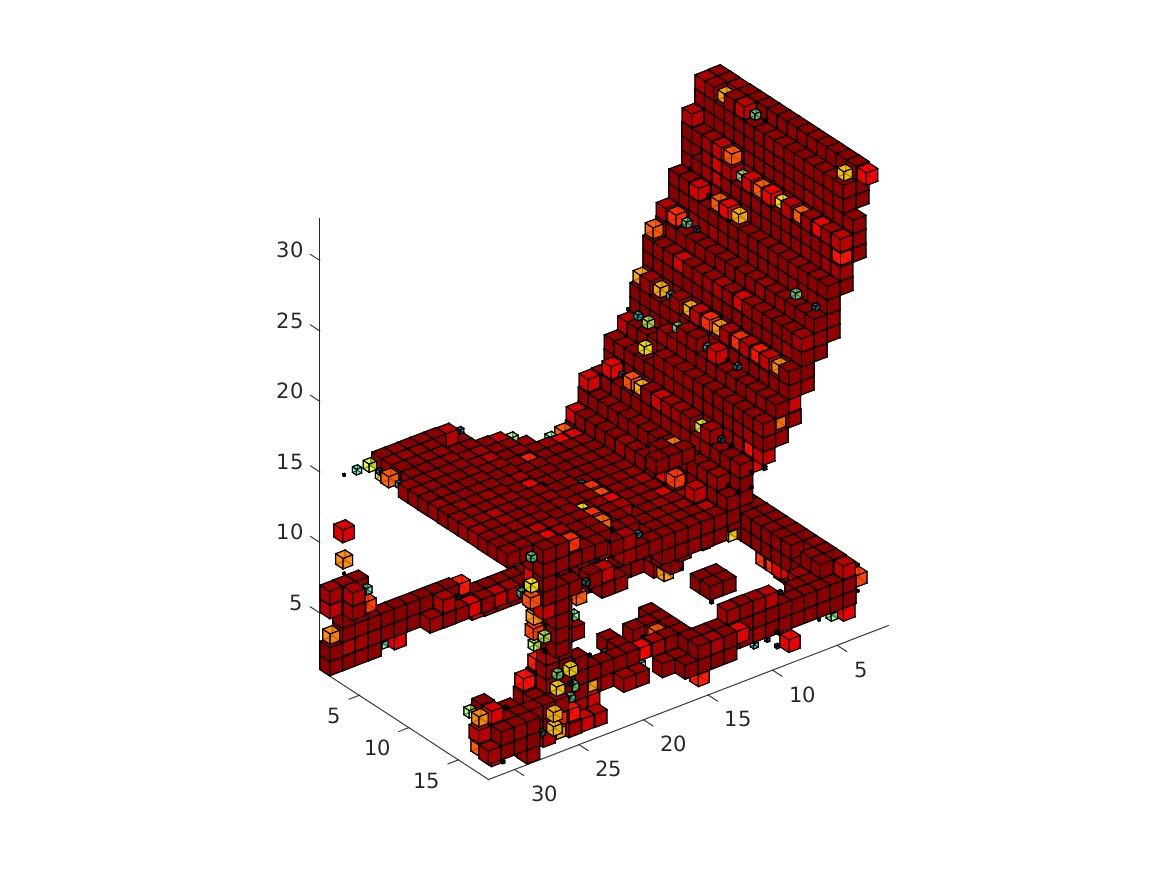 |
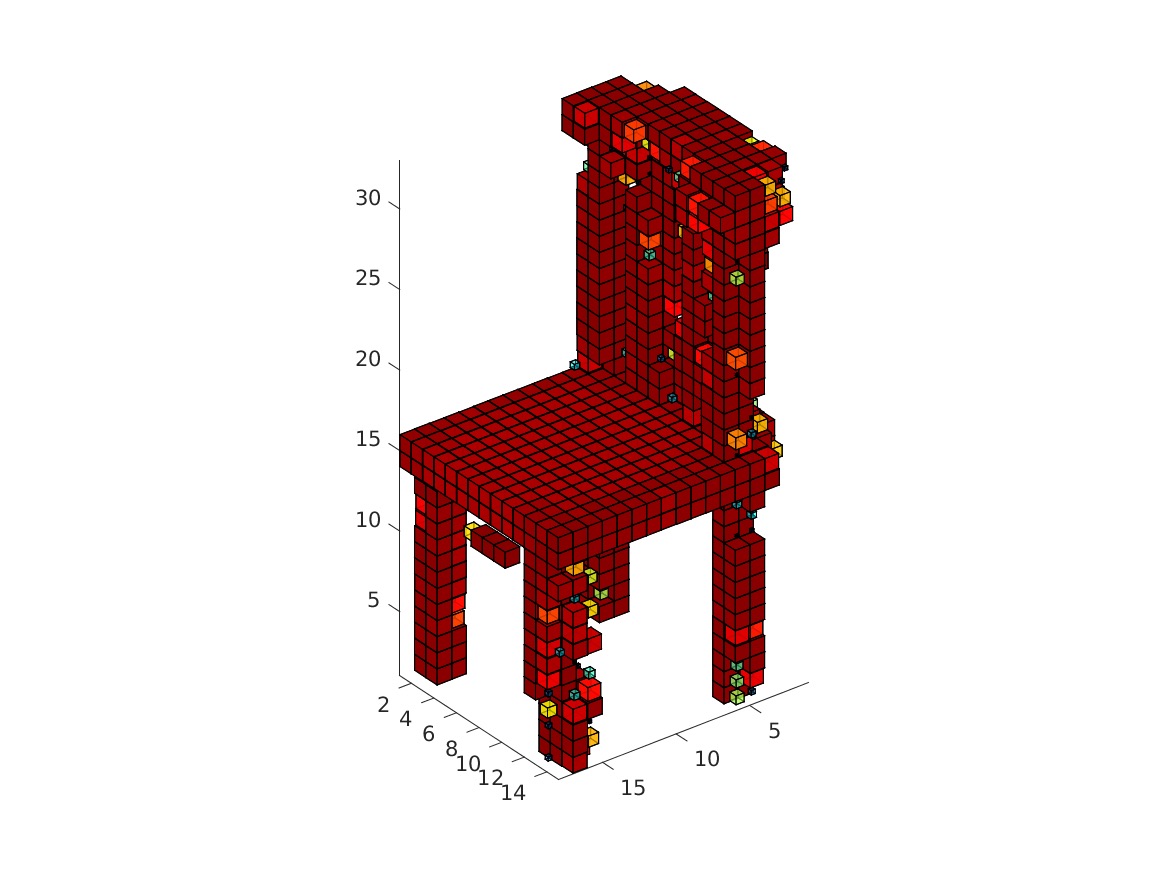 |
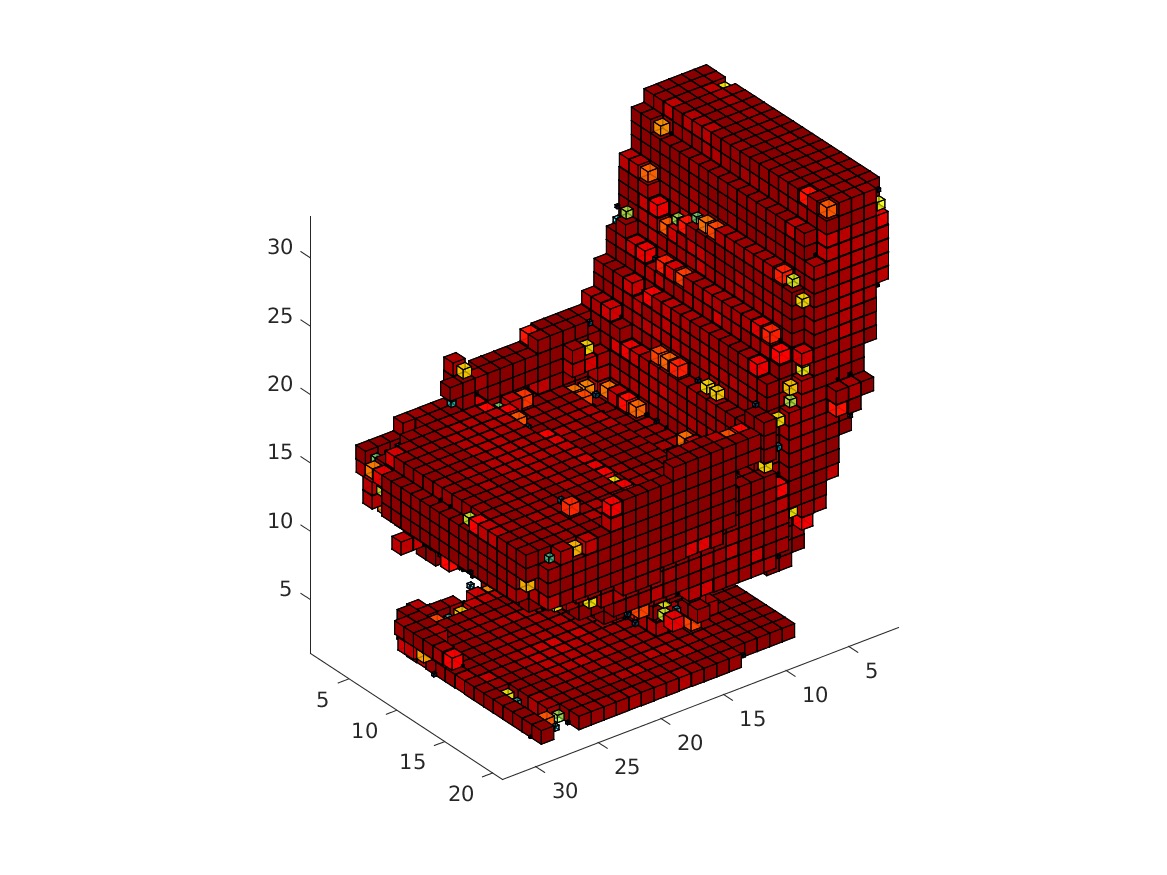 |
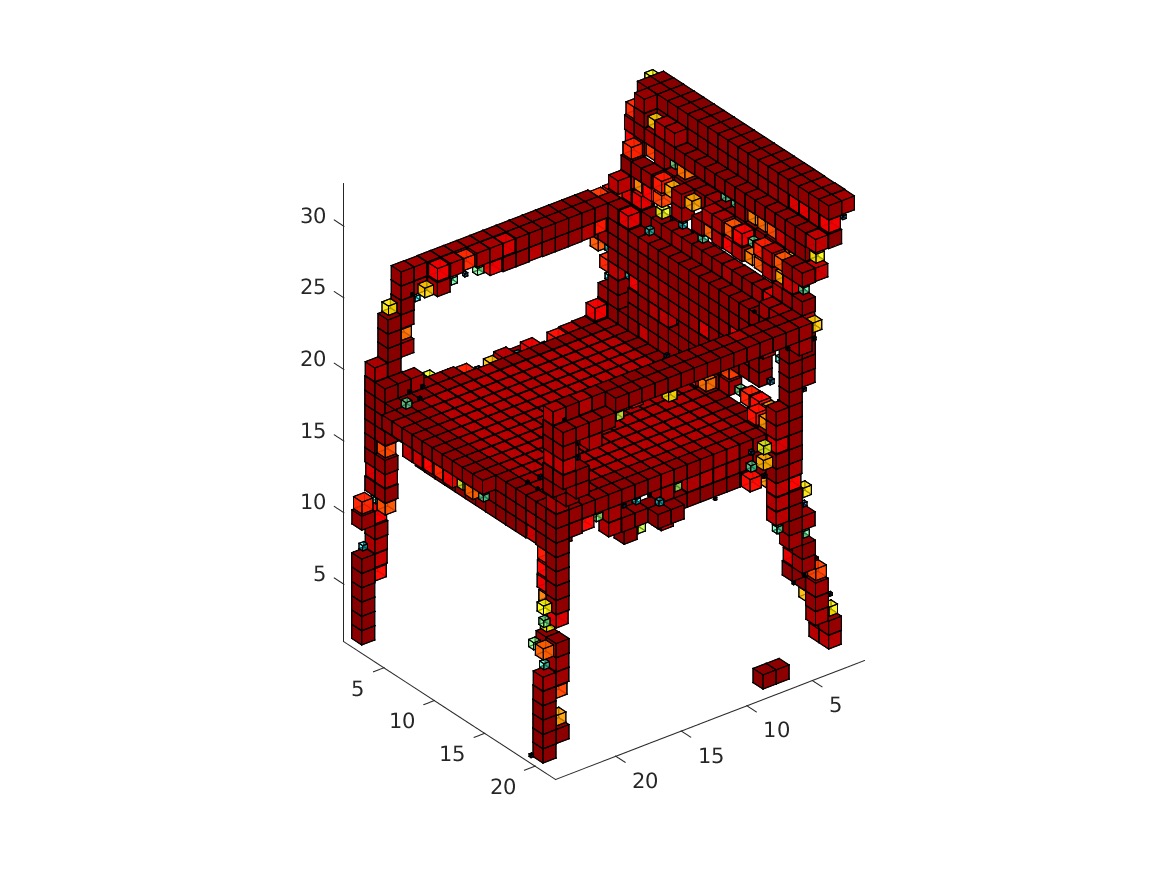 |
Python: Options for the Python visualization include
-t THRESHOLD: voxels with confidence lower than the threshold are not displayed. The default value is 0.1.-i ID: the index of objects in the inputfile that should be rendered (one based). The default value is 1.-df STEPSIZE: downsample objects via a max pooling of step STEPSIZE for efficiency. Currently supporting STEPSIZE 1, 2, and 4. The default value is 1 (i.e. no downsampling).-dm METHOD: downsample method, wheremeanstands for average pooling andmaxfor max pooling. The default is max pooling.-u BLOCK_SIZE: set the size of the voxels toBLOCK_SIZE. The default value is 0.9.-cm: whether to use a colormap to represent voxel occupancy, or to use a uniform color-mc DISTANCE: whether to keep only the maximal connected component, where voxels of distance no larger thanDISTANCEare considered connected. Set to 0 to disable this function. The default value is 3.
Usage:
python visualize.py chair_demo.mat -u 0.9 -t 0.1 -i 1 -mc 2
Reference
@inproceedings{3dgan,
title={{Learning a Probabilistic Latent Space of Object Shapes via 3D Generative-Adversarial Modeling}},
author={Wu, Jiajun and Zhang, Chengkai and Xue, Tianfan and Freeman, William T and Tenenbaum, Joshua B},
booktitle={Advances In Neural Information Processing Systems},
pages={82--90},
year={2016}
}
For any questions, please contact Jiajun Wu ([email protected]) and Chengkai Zhang ([email protected]).
